Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
H
2
N
NH
H
2
N
NH
NH
NH
O
O
O
H
H
H
N
NH
2
O
O
O
N
H
N
H
H
p
-methoxyaniline (100 mM)
pH 7 phosphate buffer
H
H
H
N
NH
2
O
O
O
O
N
H
N
H
H
N
O
O
O
OH
+
O
OH
OH
O
O
O
H
H
H
OH
O
O
O
O
N
NH
2
H
H
H
O
N
H
H
N
O
N
NH
2
H
H
H
2
N
N
H
H
N
O
O
O
O
O
H
H
O
O
O
O
O
OH
NH
NH
OH
NH
NH
H
2
N
H
2
N
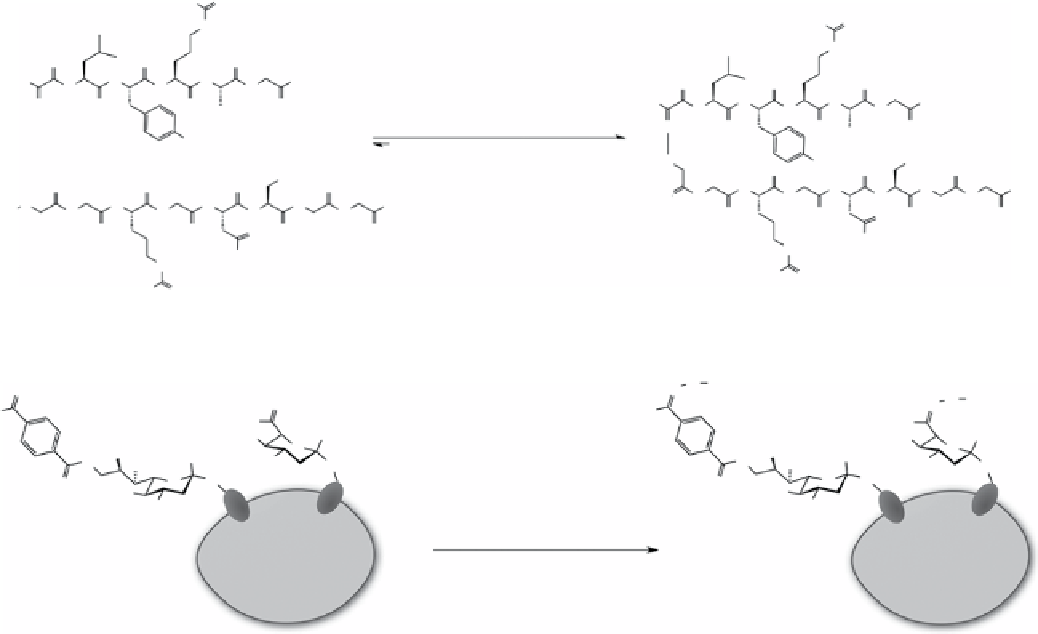
scheme 2.1
oxime ligation between glyoxylyl-LyRAg and aminooxyacetyl-gRgdSgg (1 mM) at pH 7.0.
O Biotin
O
N
Biotin
O
O
N
H
H
H
AcHN
H
AcHN
COOH
COOH
O
O
N
N
HO
HO
HOOC
HOOC
HO
HO
OH
O
OH
O
Biotin-O-NH
2
(0.1 mM)
aniline (10 mM)
pH 6.7, 4°C, 30 min
O
O
O
O
O
O
AcHN
AcHN
HO
HO
scheme 2.2
oxime ligation on cell surface with sialic acid derivatives, generated by metabolic labelling or by chemical treatment
with sodium periodate.
reactions are performed under acidic conditions (pH 4‒5) at high concentrations with a large excess of one of the reagents.
built on prior work from Schiff, Cordes, and Jencks [33-35], dawson and co-workers have found that addition of aniline
as a nucleophilic catalyst (millimolar) greatly facilitated the oxime formation reactions at much lower concentrations at
pH 7 at an observed rate constant of 0.061 M
-1
s
-1
(Scheme 2.1) [36, 37].
one prominent example of the oxime ligation was carried on living cells, wherein probes were introduced to cell surfaces
through reaction with aldehydes generated by oxidation of the glycans of cell surface glycoproteins (Scheme 2.2) [38].
The aniline-accelerated oxime ligation chemistry has been utilised in the synthesis of head-group functionalised phospho-
lipids [39], chemoselective surface immobilisation of proteins [40], and incorporation of glycans or glycopeptides to gold
nanoparticles [41]. The near-neutral conditions used in the ligation is of particular importance, while molecular probes need
to be introduced to materials containing acid-degradable bonds, such as acetalated dextran (Ac-deX) particles developed in
the Fréchet's group [10]. Alkoxyamine-functionalised peptides and fluorescent molecules were conjugated to the Ac-deX
particles efficiently through reaction of alkoxyamine and aldehyde of reducing end of the polysaccharide at pH 7.4.
Similarly, hydrazone formation between the carbonyl group and hydrazine or hydrazide can also be accelerated in the
presence of aniline [42, 43]. The utilities of aniline-catalysed hydrazone ligation have been demonstrated in a few examples -
labelling of unprotected peptide with Alexa Fluor 488 [42], modification of CdSe-ZnS core-shell quantum dots (Q dots, or
Qds) with peptides [44, 45] and immobilisation of aldehyde-modified antibodies to hydrazine-functionalised surface supports
[46]. generally, hydrazone bonds are not as stable as oxime linkages [47]. nonetheless, the degradability of a hydrazone bond
allows faster hydrolysis under acidic conditions than at physiological pH, making it a promising trigger-cleavable linkage in
drug delivery [12, 13, 16, 17, 48].
2.2.2
through reactions with azides
Azides are one of the most frequently used chemical tags for bioconjugation or labelling, due to the fact that they are not
endogenously available in biological systems, very stable under physiological conditions, and react very efficiently and
selectively once activated under various reaction conditions, such as the Staudinger ligation, Huisgen azide-alkyne cycload-
dition, and azide-cyclooctyne reaction.