Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
In nude mice, the nanogel was localised to a gastric cancer tumour using an external magnet. MRI shows a darkening of
the tumour, indicating the presence of the particles after 8 h. NIRF imaging shows that the agent localises in the tumour bet-
ween 0 and 6 h. Over the period of one month, the tumour was treated with a combination of the chlorin nanogel, magnetic
targeting, and irradiation, and did not grow in size in contrast to the control groups.
16.3.3
tumour targeting using nIr-MrI bimodal agents
In order to improve diagnostics and therapeutics, the efficiency of tumour targeting must be optimised. Various strategies
have been employed, including using targeting peptides, antibodies, and reliance on the EPR effect. Tumour targeting can be
evaluated using multimodal imaging of nanoparticle platforms
in vivo
.
High-density lipoprotein (HDL) is a biologically endogenous nanoparticle that can be readily modified [44, 45]. In this
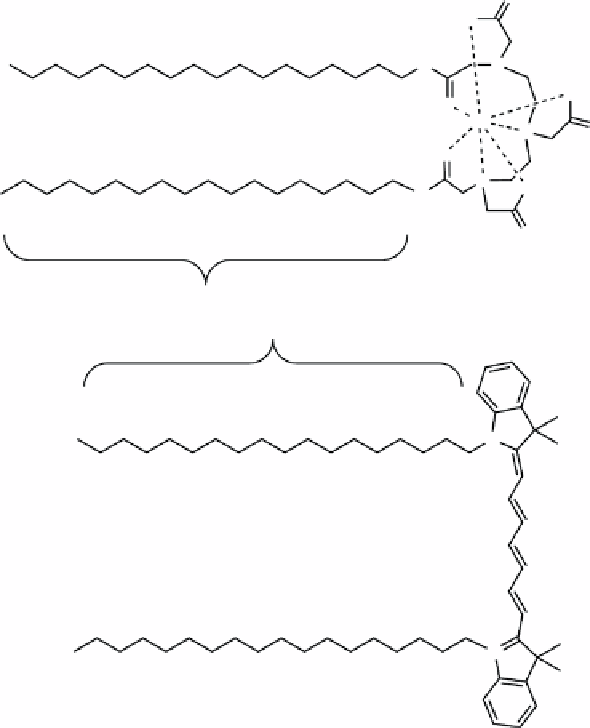
report, HDL was reconstituted with a hydrophobic Gd chelate (gadolinium diethylenetriaminepentaacetate-di(stearylamide),
or Gd-DTPA-DSA) and 1,1-dioctadecyl-3,3,3′,3′-tetramethylindotricarbocyanine iodide (DiR), a NIR dye (Figure 16.10)
[46]. Finally, either the targeting cyclic peptide cRGD or the control peptide cRAD was conjugated to the particle through
formation of a disulfide bond (Scheme 16.7). The r
1
was found to be 8.5 mM
-1
s
-1
with the particles being approximately
12 nm in diameter.
In vitro
tests with human umbilical vascular endothelial cells show the RGD targeting is specific [46].
In vivo
tests, how-
ever, show that rHDL, rHDL-RGD, and rHDL-RAD all accumulate in the tumour over 24 h, likely due to the EPR effect.
However, confocal microscopy of tumour sections shows that the accumulation patterns are different. NIRFI also showed
that the binding kinetics
in vivo
were different for the three HDL platforms.
Gliosarcoma is a particularly difficult cancer to treat and the subject of increasing investigation [47]. SPIONs with
a silica shell, PEG coating, and amine functional groups were modified to conjugate chlorotoxin (CTX), a targeting
O
O
N
N
O
O
Gd
O
N
O
N
O
H
O
Hydrophobic regions for membrane labelling
N
+
N
fIGure 16.10
Structures of GdDTPA-DSA and DiR. The long hydrophobic alkyl chains are designed to optimise membrane
labelling.