Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
(a)
(b)
(c)
200 nm
200 nm
100 nm
(d)
(e)
(f)
50 nm
100 nm
100 nm
(g)
(h)
10 nm
50 nm
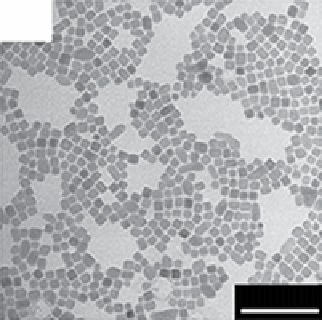
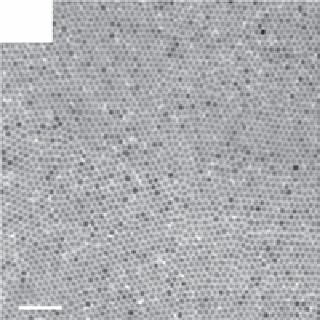
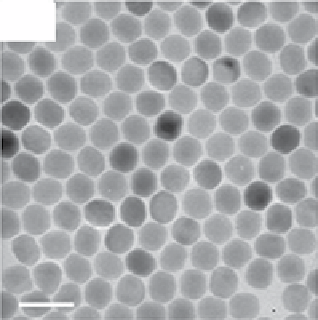
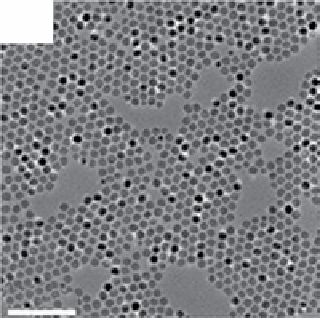
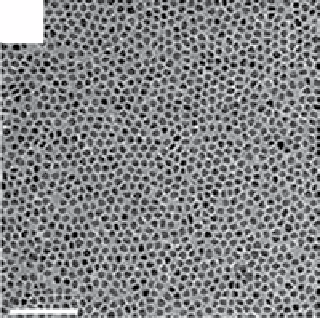
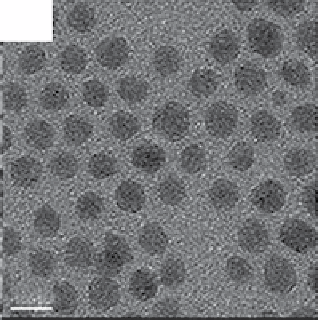
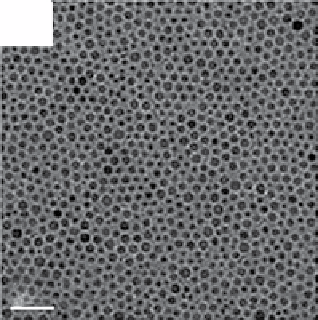
FIgure 13.2
TEm images of the upconversion nanocrystals obtained by hydrothermal methods (a, b), thermal decomposition in high-
boiling solvents (c, d), and thermal decomposition methods (e-h). Reprinted with permission from refs. [14-18]. Copyright 2007 American
Chemical Society, 2008 IoP Publishing Ltd., 2006 American Chemical Society, 2010 American Chemical Society, 2006 Wiley-vCH
verlag gmbH&Co. KgaA, Weinheim.
based UCNPs in oA and 1-octadecence (oDE) [15]. The shape and size of UCNPs can also be controlled by fine-tuning the
composition of the solvents.
In addition, Li and co-workers developed a general method to synthesise nano-sized materials by utilising the interfaces
of the liquid, solid, and solution (LSS) phases [10, 24]. They used this LSS method to fabricate a series of inorganic nano-
crystals with controllable size and shape. Ln-UCNPs can also be obtained by such a general method.
In addition to the hydrothermal and thermal decomposition methods, other methods such as sol-gel [25, 26], combustion,
[27] ionic liquid-based synthesis [28-30], and microwave-assisted synthesis [31, 32] are also used for the synthesis of
Ln-UCNPs. The principles and controlling methods are similar to those used in the hydrothermal and thermal decomposition
methods.