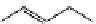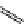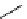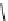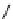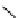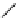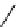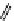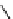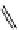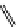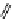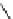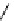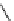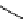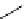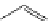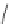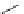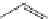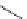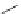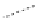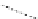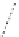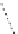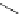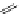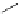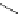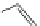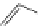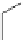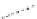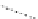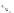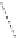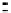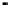Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
N
N
N
N
R
N
N
R
CO
2
H
HO
2
C
OMe
O
3
R=
CO
2
H
O
O
2
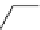
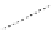
FigUre 12.19
An example of a ditopic ligand used for the formation of bimetallic helical complexes.
-
NH
2
NH
2
-
OH
O
H
2
O
2
/
Horseradish
peroxidase
N
N
N
N
N
N
N
N
N
N
Tb
Tb
O
O
O
N
O
N
N
N
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
Strongly emissive
Weakly emissive
FigUre 12.20
The two forms of the Tb
III
complex.
In tandem with the diverse development of myriad cyclen-derived Ln
III
complexes, an important, alternative class of
species conceived by Bünzli are luminescent bimetallic, triple-stranded helical complexes of the general formula [Ln
III
2
L
3
].
Based on chromophoric, hexadentate ditopic ligands (Figure 12.19), the complexes are formed through a self-assembly pro-
cess at room temperature. These emissive Ln
III
complexes can also be bioconjugated with targeting vectors such as avidin,
or monoclonal antibodies, allowing recognition of proteins expressed on the surface of breast cancer cells. The use of TRLM
improves the signal-to-reference ratios, allowing high performance screening of cells and tissues; the diagnostic implica-
tions of this approach are significant to pathology [57].
The development of a responsive Tb
III
-based probe for imaging hydrogen peroxide evolution in plant tissue (Figure 12.20)
further highlights the utility of time-resolved imaging experiments. The starting Tb
III
complex is essentially non-emissive,
due to intramolecular quenching pathways within the terpyridine-based ligand; reaction with H
2
O
2
, in the presence of
hydrogen peroxidase, cleaves a diaminophenylether unit, switching on visible luminescence from the Tb
III
ion. The respon-
siveness of the complex was assessed
in vitro
using TRLM studies on tobacco leaf epidermal tissues. The obtained images
are background free, with autofluorescence from the tobacco cells effectively suppressed, and show remarkable detail and
spatial resolution [58].
12.3.4
Cellular imaging with
f
f-Metal Complexes
The following discussion focuses on the utility of emissive Ln
III
complexes as intracellular optical imaging agents and is
subdivided according to ligand classification. It is important to note that many of the imaging studies described below are
accompanied by additional investigations, which are not dealt with in detail here, including the physiological relevance of
the probes, such as protein affinity (secondary confirmation can be alternatively obtained through companion relaxivity