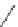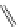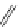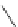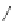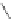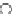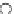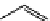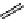Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
N
N
+
-
I
4-(4-(Dimethylamino)styryl)-N-methylpyridinium iodide (DASPMI)
Styryl-based dyes
λ
abs
(nm)
λ
em
(nm)
Remarks
DASPMI
475
605
MeOH
MeOH,
emit at 598 nm when bound to
biomembranes
FM1-43
512
626
FM4-64
560
767
MeOH
fIgure 11.18
DASPMI and the FM series of plasma membrane stains.
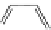
O
O
Coumarin
Coumarin-based dyes
λ
abs
(nm)
λ
em
(nm)
Remarks
Calcein blue
360
449
pH 9.0
DACM
383
463
MeOH
AMCA succinimidyl ester
354
440
MeOH
fIgure 11.19
Structure of coumarin.
are laser dyes. They are also useful luminophores for bioimaging because of their biocompatibility and their higher energy
fluorescence (λ
max
< 500 nm), which makes them complementary energy donors to fluorescein-based acceptors in FrET
processes [106-109]. Calcein Blue, consisting of a coumarin luminophore linked with a calcium-chelating methyliminodi-
acetic acid functionality, is used as a marker of bone growth and to identify microcracks in bones [110, 111]. The
N
-(7-
dimethylamino-4-methylcoumarin-3-yl) maleimide (DACM) and 7-hydroxycoumarin-3-carboxylic acid succinimidyl ester
(AMCA) are two commonly used fluoro-tagging agents for peptides, proteins, antibodies, and other biomolecules.
11.3.6
reactive chloride dyes
4-Chloro-7-nitrobenzo-2-oxa-1,3-diazole (NBD chloride) is a benzofurazan heterocycle with a reactive chloro group
(Figure 11.20). It is a useful fluoro-tag for a wide range of biomolecules and xenobiotics because it is able to form covalent
linkages with exposed amino, hydroxyl, and thiol moieties. It is biocompatible with live cells. The fluoro-tagged phospho-
lipids, NBD-phospholipids, have been used to trace lipid metabolism in yeast [112]. The fluoro-tagged peptides, NBD-
peptides, have been used to study the adsorptive endocytosis process of small peptides in live cells [113]. Dansyl chloride is
a widely adopted luminophore for
in vitro
and
in vivo
fluoro-tagging of peptides, proteins, and antibodies. It has a naphtha-
lene ring and a reactive sulfonyl chloride substituent [114-116] (Figure 11.20).
11.3.7
bodIpy and Its derivatives
Any discussion of organic-based luminophores for biomedical and imaging applications would not be complete without an
introduction to the BODIPY luminophore and its derivatives. BODIPY is the acronym of boron dipyrromethine; its full
nomenclature is 4,4-difluoro-4-bora-3a,4a-diaza-
s
-indacene. It is a very popular luminophore for fluoro-tagging and bioim-
aging applications due to its unique advantageous photophysical properties, such as near 100% photoluminescent quantum
yield in aqueous media, environment-independent fluorescence, ease of derivatisation, and the ease of fine-tuning of fluo-
rescence wavelength by the introduction of different substituents [117-119].
In fact, in spectroscopic and spectrofluorometric terms, commercially available BODIPY derivatives (Figure 11.21) have
already covered the full range of the visible spectrum. reactive functionalities have been grafted onto the luminophore in
order to generate fluoro-tags, which are capable of labelling biomolecules and xenobiotics. Special substituents have also
been incorporated onto the luminophore to bring about specific responsive properties toward targeted stimulations and enzy-
matic/analyte activities (Figure 11.22) [120-122].