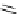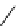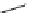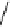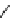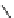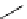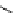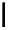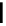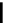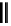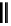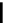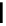Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
fluorescent probes bearing basic amine groups have been developed for the staining of lysosomes (Figure 11.3). Protonation
of the amine functionalities within the acidic microenvironment of lysosomes switches on their fluorescence due to the sup-
pression of the photo-induced electron transfer (PET) processes (the PET mechanism will be introduced in a later section).
This also converts the probes into cationic species and assists their retention in the lysosomes.
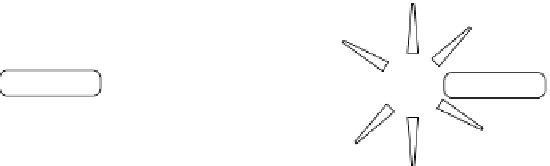
Non-covalent associating fluorescent probes that give signals upon binding with their analytes (molecular recognition)
are referred to as fluorescent responsive probes (or chemosensors). This type of fluorescent probe is generally composed of
two major components, a receptor for molecular recognition and a fluorophore as the signalling source, which are linked
together with an appropriate spacer, forming the well-known fluorophore-spacer-receptor motif. Alternatively, the receptor
and the fluorophore can be integrated without a spacer (Figure 11.4). When the analyte is bound to the receptor, the physio-
chemical properties of the fluorophore, such as fluorescence intensity, emission wavelength, and fluorescence lifetime, will
be changed via different photophysical mechanisms. These changes provide a signal that indicates the recognition event. A
variety of fluorescent biosensors have been developed for specific binding with biologically important cations (such as Mg
2+
,
Zn
2+
, Cu
2+
, Ca
2+
, K
+
, and Na
+
), anions (such as phosphate, citrate, and carbonate) and neutral molecules.
N
N
· 4HCl
O
N
N
B
N
F
F
H
NH
N
H
Lysotracker blue DND-22
Lysotracker red DND-99
Cl
-
N
+
N
O
O
N
N
B
N
F
F
H
Cl
Lysotracker yellow HCK-123
Lysotracker green DND-26
fIgure 11.3
Structures of selected fluorescent probes for lysosomal staining.
(a)
(b)
Spacer
Fluorophore
Receptor
Fluorophore
Receptor
(c)
= Analyte
Spacer
Spacer
Biosensor
Change in physical properties
fIgure 11.4
(a) The spaced and (b) integrated model for fluorescent sensors. (c) The schematic representation of fluorescent sensing.