Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
1.4.2
Advantages and limitations
cT imaging provides fast and high spatial resolution images that allow fine visualization of anatomical details. As a diagnostic
technique, it is often used to detect or confirm cancerous tumours by providing detailed information such as the size and
location of the tumour to help planning for radiation therapy or surgery. one of the major advantages of cT is that it could
be combined with other imaging modalities such as PET and MrI to provide other information such as dynamic and meta-
bolic data (Figure 1.12). However, repeated cT imaging carries health risks to the patient due to exposure to non-negligible
radiation dosage.
Another problem is that the scanning procedure can be quite time-consuming and may require up to an hour to
complete. This could cause discomfort to patients in some cases. In general, cT imaging is a pain-free procedure, and
it is often incorporated into other techniques to create powerful multimodal imaging modalities to give improved
sensitivity and resolution for diagnosis, especially in cancer. The improvement in images due to the use of combined
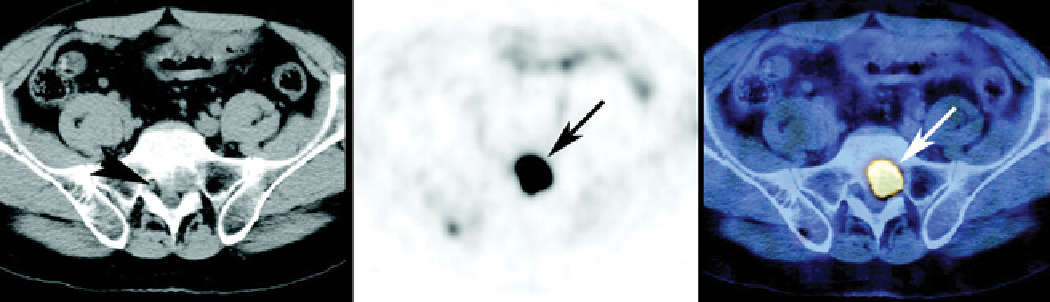
techniques such as cT and PET are shown in Figure 1.13. It is apparent that the combined use of cT and PET
provides more information on tumours, such as their location and size as well as growth and metabolic activity of
tissues [23].
168 cm
80 cm
200 cm
CT
PET
156 cm
Dual-modality imaging range
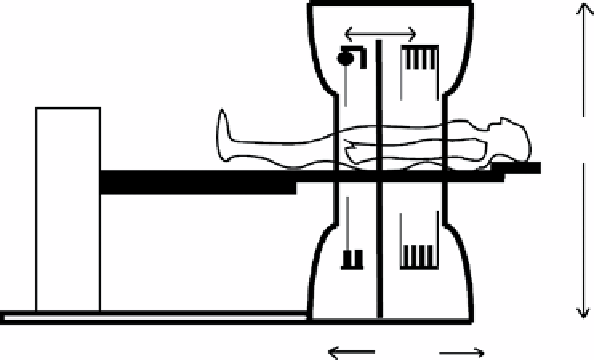
FIgure 1.12
Diagram showing a typical cT-PET instrument [22].
FIgure 1.13
Left: Image from a cT scan; Middle: Image from a PET scan; right: Image from a cT-PET scan [23]. (
See insert for
colour representation of the figure.)
)