Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
Parasagittal
RMS path
2 mm
2 mm
Day 0-1
Day 4
Day 7
Day 21
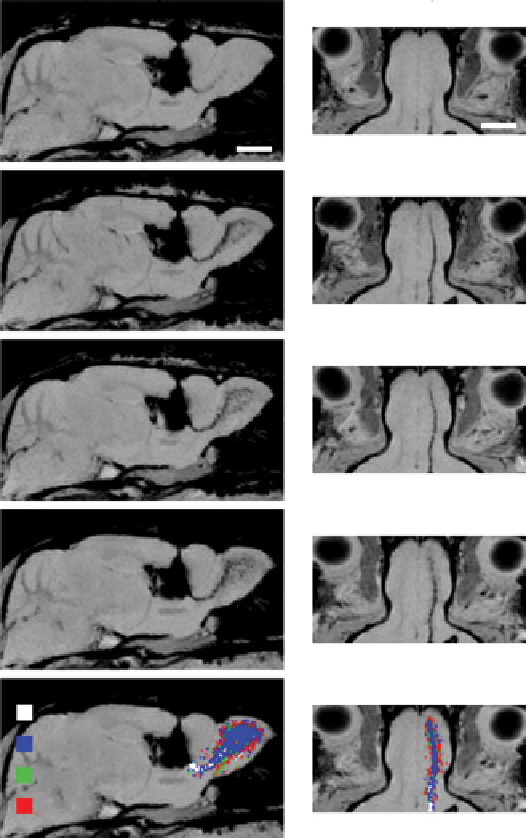
FIgure 9.13
Distribution of magnetic nanoparticles in the olfactory bulb (OB). Parasagittal and RMs reformatted images are shown
at Days 0-1 (combining images from 3 to 24 h post-injection), Day 4, Day 7, and Day 21. each image is representative of a composite of
three or more individual animals. Distribution through the bulb occurs primarily in the parasagittal plane (left column) with relatively little
motion laterally (as seen in the right column). Images obtained with permission from Ref. [160].
mutant (eGFRvIII) present on human glioblastoma multiforme was coupled to the nanoparticles. In this strategy, the
antibody is coupled to the nanoparticles in a random way through a ε amino group of the side chain of a lysine. Through
this random coupling, part of the antibodies will probably lose their bioactivity because their recognition areas will be
blocked or hindered, but the overall population of nanoparticles will gain specificity. Apart from the preparation of
nanoparticles, the other main problem encountered was the delivery of the probes to the tumour inside the brain. The
blood-brain barrier (BBB) is a closely packed layer of cells that prevents the delivery of most products inside the brain.
To overcome this barrier they used a procedure called convection-enhanced delivery (CeD) which is a minimally invasive
surgical procedure that provides fluid convection in the brain by a pressure gradient that bypasses the BBB. The group
demonstrated that glioblastomas could be labelled and visualised by MRI
in vivo
in mice with functionalised magnetic
nanoparticles and that the use of the antibody anti eGFR in the nanoparticles also produces a significant increase in the
animal survival.
sosnovik et al. [162] reported the application of iron oxide-based T
2
contrast agents to image cardiomyocyte apoptosis
and necrosis
in vivo
in an ischemia model. To do so [139], an MRI probe was prepared consisting of iron oxide nanoparticles
functionalised with a protein called annexin V. Annexin V is a relatively small protein that binds strongly and with high
specificity to phosphatidylserine (Ps). The group prepared first amine-functionalised cross-linked iron oxide nanoparticles
(CLIO) following co-precipitation protocols and using dextran as the ligand. These were then reacted with sPDP