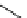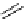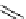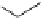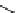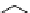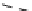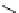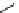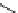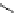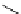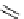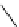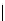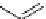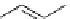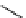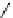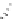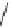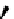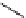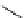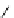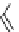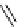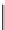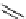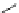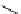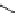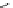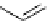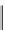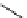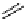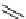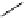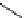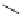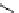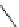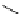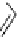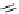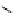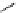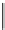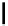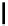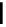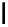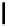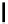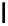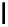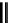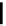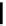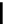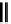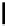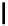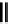Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
124
I
124
I-nucleophilic
exchange
O
2
N
I
O
2
N
N
N
OH
OH
OH
N
N
O
[
124
I]NaI, DMF
O
OH
Δ
[
124
I]-IAZGP
OH
OH
F
F
124
I
I
[
124
I]NaI, CuSO
4
,
(NH
4
)
2
SO
4
, MeOH/H
2
O
F
HO
F
HO
O
O
60 min, 140°C
[
124
I]-dRFIB
OH
OH
NH
[
124
I]NaI, CuSO
4
,
SnSO
4
, citric acid,
dihydroxybenzoic acid
30 min, 130°C
NH
124
I
H
NH
2
I
H
NH
2
[
124
I]-MIBG
O
124
I-electrophilic
substitution
O
124
I
NH
NH
[
124
I]NaI, iodogen
©
N
O
[
124
I]-FIAU
N
O
HO
HO
F
F
O
O
OH
OH
124
I
Sn(CH
3
)
3
N
OH
N
OH
HN
HN
[
124
I]NaI, Iodogen
©
H
O
H
O
O
O
m-[
124
I]-IPPM
OH
OH
O
124
I-prosthetic
groups
O
a) [
124
I]NaI, Iodogen
©
pH 6.5
b) VG76e antibody
coupling, pH 8.5, 0°C
124
I
VG76e
O
H
N
O
HO
O
[
124
I]I-HPP-VG76e
HO
SHPP
O
O
O
a) [
124
I]NaI
chloramine T
b) Annexin-V
coupling
N
Annexin-V
O
H
O
124
I
Sn(CH
3
)
3
m-[
124
I]-IBA-Annexin-V
SIB
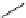
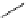
fIgure 5.18
Examples of common
124
I-radioiodination protocols, grouped into nucleophilic exchange, electrophilic substitution, and
prosthetic group labelling.
5.8.4
stability of
124
Iodine-Based radiopharmaceuticals
As with radiometal-containing radiopharmaceuticals,
in vivo
stability is of great concern with
124
I-based radiopharmaceuti-
cals. With radioiodinated agents the issue is less straightforward, because decomposition is likely to occur through the
normal biochemical metabolism of the parent drug, regardless of the stability and inertness of the carbon-radioiodine bond.
due to its long half-life and β
+
emission,
124
I is an ideal candidate for pharmacological studies in drug development and can
be used to monitor the pharmacokinetics of labelled drugs
in vivo
through PET imaging over long periods of time [206]. One