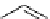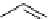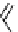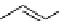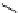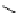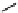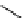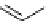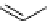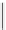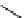Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
O
*
H
H
C-11 urea
N
3
NH
2
N
3
O
11
CO / Rh(I) Cat.
*
H
O
CH
3
CH
2
OH
C-11 carbamate
CH
3
CH
2
OH
N
2
O
H
OCH
2
CH
3
O
O
H
3
CH
2
CO
*
OCH
2
CH
3
C-11 malonate
selected rhodium-mediated [
11
C]carbonylation reactions forming [
carbonyl
-
11
C]urea, carbamate, and malonate compounds.
scheme 4.22
O
R H
*
C-11 carboxylic acids
RI
H
2
O
O
RI
11
CO /
hv
micro autoclave
R′
RO
R′OH
*
C-11 esters
R=alkyl group
RI
R′NH
2
O
R′
R
H
*
C-11 amides
scheme 4.23
synthesis of [
carbonyl
-
11
C]-labelled aliphatic carboxylic acids, esters, and amides in high pressure photo-initiated car-
bonylation system.
4.3
nItrogen-13 chemIstry
Nitrogen-13 is produced by the nuclear reaction
16
O(p,α)
13
N via the proton irradiation of H
2
O creating a mixture of [
13
N]
ammonia, [
13
N]nitrogen, [
13
N]nitrite, and [
13
N]nitrate [126, 127]. [
13
N]nitrite and [
13
N]nitrate are formed predominately;
however, [
13
N]ammonia is the most desirable
13
N product because of its direct application in PET myocardial perfusion
studies [128] and its potential for further chemical reactions. The synthesis of [
13
N]ammonia is typically achieved outside
the target via the reduction of
13
NO
x
s using Devarda's alloy [129-131] or TiCl
3
; [132] however, in-target [
13
N]ammonia pro-
duction is also accessible. One reported method uses an ethanol/hydrogen gas in-target [133, 134], while another reports
high specific activity of
13
NH
3
production by proton irradiation of H
2
O in the presence of 10 mM ethanol saturated with
oxygen gas [131] (scheme 4.24).