Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
MOFs are highly crystalline inorganic-organic hybrid structures that
contain metal clusters or ions (secondary building units, or SBUs) as nodes
and organic ligands as linkers. When guest molecules (solvent) occupying
the pores are removed during solvent exchange and heating under vacuum,
porous structure of MOFs can be achieved without destabilizing the frame,
and hydrogen molecules can be adsorbed onto the surface of the pores by
physisorption. Compared with traditional zeolites and porous carbon materi-
als, MOFs have very high number of pores and large surface area that allow
higher hydrogen uptake in a given volume. Thus, research interests in hydro-
gen storage using MOFs have been growing since 2003 when the first MOF-
based hydrogen storage was introduced [44]. Since there are infinite geometric
and chemical variations of MOFs based on different combinations of SBUs
and linkers, many researches have explored what combination will provide
the maximum hydrogen uptake by varying materials of metal ions and
linkers.
In 2006, hydrogen storage concentrations of up to 7.5 wt% in MOF-74
has been achieved at a low temperature of 77 K [45]. In 2009, a higher
storage concentration (10 wt%) at 77 bar (1117 psi) and 77 K with MOF
NOTT-112 was reported [46]. Most studies of hydrogen storage in MOFs
have been conducted at a temperature of 77 K and a pressure of 1 bar because
such condition is commonly available and the binding energy between hydro-
gen and MOF is large compared with the thermal energy that can allow high
hydrogen uptake capacity. The amount of hydrogen uptake depends on a
number of factors, such as surface area, pore size, catenation, ligand struc-
ture, spillover, and sample purity.
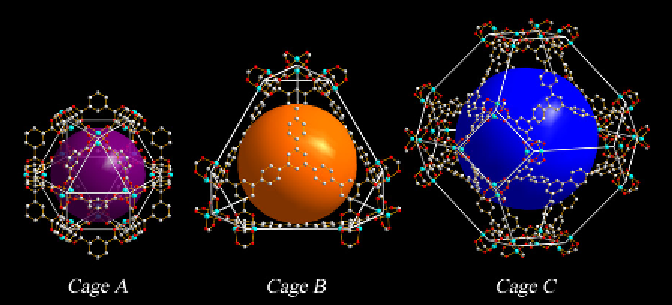
FIGURE 7.7
Different cages in the crystal structure of NOTT-112. Copper: blue-green; carbon: grey;
oxygen: red. Water molecules and H atoms are omitted for clarity.
Source
: Reproduced with permission
from Yan et al. [46]. (See color insert.)
Search WWH ::

Custom Search