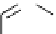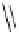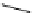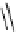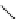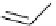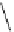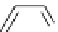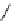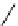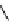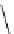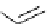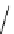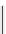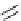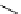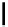Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
R
1
OH
O
Yb
t
Bu
N
N
N
O
H
N
H
N
t
Bu
R
2
R
3
N
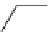
Figure 3.7
Supposed transition state without triflate anion
78
C in the presence of a catalytic amount of copper salts
to afford the corresponding optically active homoallyl alcohols in high yield (81-99%) and
high enantioselectivities (89-94%ee) [78].
aldehydes or reactive ketones at
3.3.14.9 Ytterbium
Achiral ytterbium Lewis acid was prepared from ytterbium triflate [Yb(OTf)
3
], (R)-(
)-
1,1
0
-bis(2-naphthol) (BINOL) and DBU (1), and subjected to aza Diels-Alder reactions of
achiral imines (N-benzylidene-2-hydroxyanilines) and achiral dienophiles [79]. In this
reaction the use of a chiral Lewis acid containing 1,3,5-trimethylpiperidine instead of 1
resulted in a lowering of the enantiomeric excess of adduct. Thus, the phenolic hydrogen of
the imine interacts with DBU (1) in transition state, as shown in Figure 3.7, to increase the
selectivity.
þ
3.3.15 Michael Reaction
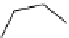
Four enantiopure hydroxyamidines were prepared from (S)-pyroglutamic acid by coupling
of an (S)-malic acid derived N-allyliminium ion with
-naphthol, and from an (S)-serine-
derived imide [80] (Figure 3.8). Unfortunately, their application to the catalytic Michael
b
H
H
H
H
Ph
NN
NN
NN
OH
NN
OH
OH
Ph
HO
Figure 3.8
Structures of chiral hydroxyamidines