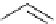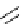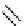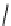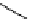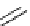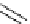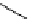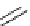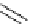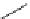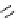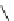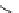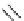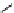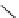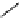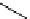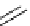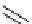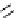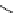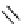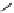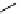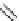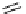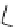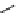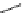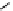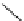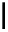Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
NMe
2
NMe
2
NMe
2
NMe
2
Me
2
N
NMe
2
NMe
2
NMe
2
Me
2
N
P
P
N
N
NMe
2
Me
2
N
N
N
NMe
2
DMAN
DMEGN
HMPN
APA 245.1 calc
p
K
a
18.2 expt
APA 263.8 calc
p
K
a
25.1 expt
APA 273.9 calc
p
K
a
29.9 expt
NMe
2
NMe
2
NMe
2
NMe
2
NMe
2
NMe
2
Me
2
N
N
N
N
N
NMe
2
P
P
NMe
2
N
N
N
N
NMe
2
NMe
2
NMe
2
137
APA 305.4 calc
p
K
a
44.8 calc
Figure 2.14
Structures of DMAN-related guanidinophosphazene bases
thus shortens to about 2 A
in azaphosphatranes [98]. Basicity measurements have shown
that proazaphosphatranes are exceedingly strong nonionic Brønsted bases. They are unique
in that, unlike all of the commonly used nonionic bases (including the phosphazene series),
they are protonated on their phosphorus atom rather than on one of their nitrogen atoms.
High basicity is the combination of the degree of delocalization of the bridgehead nitrogen
lone pair into a three-centre, four-electron bond system along the molecular axis and partial
donation of electron density from the axial nitrogen enhances electron density on
phosphorus atom [99].
The originally reported pK
a
value of 41.2 for 139, which was in the vicinity of that for P3
and P4 phosphazene bases, was recently re-evaluated at 32.82 in acetonitrile by UV-Vis
spectrophotometric titration, as shown in Table 2.13 [100]. This value is similar to the
phosphazene base P
2
-Et (pK
a
¼
32.74). The pK
a
values for 139-141 determined in
acetonitrile by
31
P NMR spectroscopy fall in the same range (32.84-33.63). X-ray-
determined P-N
ax
bond distances of 141 and 142 are 2.037 and 1.958 A
. An even larger
pK
a
value for 143 was determined by
31
P NMR spectroscopy in acetonitrile (34.49) [101],
while the parent compound 138 has a pK
a
value of 29.6 inDMSO [102]. The greater stability
and therefore weaker acidity of cation 138H
þ
compared with 139 (R
¼
CH
3
) and 144