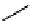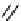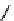Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
R
HN
H
N
NH
NH
2
N
H
NH
HO
2
C
N
HO
2
C
N
Me
O
NH
Me
ectoine (
9
)
noformycin (
10
)
pyrostatin A (
7
): R = OH
pyrostatin B (
8
): R = H
X
H
2
C
H
N
H
N
2
H
2
H
HN
HN
N
H
N
H
O
Me
O
Me
OH
Me
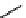
11
: X = CH
2
;
12
: X = 2H
13
Figure 10.3 Structures of pyrostatins A and B (7-8), ectoine (9) and other iminopyrrolidine
natural products
10.2.2 Natural Amidines from Marine Invertebrates
10.2.2.1 Flustramine C
Flustramine C (14) was isolated from bryozoan Flustra foliacea (L.) [29,30]. This
compound possesses the amidine moiety in brominated pyrroloindole structure with
1,1-dimethylallyl group (Figure 10.4). It has been suggested that the Flustra alkaloids
are important for the bryozoan by controlling bacterial growth on its surface [31]. This
compound is levorotatory [32], however, the absolute configuration has not been deter-
mined yet. Total syntheses of racemic one were achieved by three groups [33-35].
10.2.2.2
Perophoramidine
Perophoramidine (15), halogenated alkaloid, was isolated from the Philippine ascidian
Perophora namei Hartmeyer andMichaelson (Perophoridae) [36a]. This compound contains
fused hexahydropyrrolopyridine, indole and dihydroquinoline rings. Amidine parts exist at
the fusing part of the indole and quinoline rings. The stereochemistry was determined by
Me
Cl
Me
N
N
Me
N
Me
N
Cl
H
Br
Br
N
flustramine C (
14
)
perophoramidine (
15
)
Figure 10.4
Structures of flustramine C (14) and perophoramidine (15)