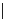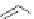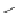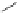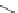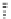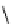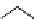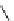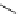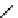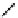Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
Table 4.5 Asymmetric Michael reaction between t-butyl glycinate Schiff base and active
vinyl compounds in the presence of the guanidine 17
17
(0.2 equiv)
Ph
Ph
X
X
+
Ph
N
CO
2
t
Bu
CO
2
t
Bu
Ph
N
20 ºC
(3.6 equiv)
(1 equiv)
THF or without a solvent
Ph
Run
17
X
Solvent
Time
Yield (%)
ee (%)
1
THF
OH
6 d
90
96
17a
COMe
N
2
—
15 h
90
80
THF
3
7 d
15
79
Me
NN
Me
17a
CO
2
Et
—3 d
85
97
4
THF
5
7 d
62
90
Ar
Ar
17b
CO
2
Et
—5 d
79
97
6
THF
7
NR
a
17a
: Ar = Ph
17b
: Ar = 2-methylphenyl
5 d
—
17a
CN
—5 d
79
55
8
a
No reaction.
on DMC chemistry, especially under solvent-free condition (Table 4.5). Thus, an
(R)-adduct was given in 85% yield with 97% ee [51]. It is noted that MVK is reactive
enough even in solution [51] and that modification of the phenyl pendant in the guanidine
skeleton 17b to 2-methylphenyl ones accelerates the addition reaction [52]. A bicyclic
network system through two hydrogen bonds and one CH-
interaction in the transition
state is proposed as playing an important role for high asymmetric induction [52].
The same guanidine 17a also works as a catalyst in the Michael reactions of cyclo-
pentenone and benzyl malonate (or
p
-methylmalonate). However, moderate selectivity was
observed even under solvent-free conditions [53].
An axially chiral and highly hindered binaphthyl-derived guanidine catalyst 18a with an
internal guanidine unit (Figure 4.6) facilitates the highly enantioselective 1,4-addition
a
R
2
t
Bu
R
2
N
a
: R
1
= Me, R
2
=
N-R
1
t
Bu
H
b
: R
1
= Bu, R
2
=
t
Bu
R
2
18
R
2
Figure 4.6 The structures of representative axial chiral guanidines 18 with an internal
guanidine system