Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
(A)
1
st
measurement
2
nd
measurement
= 2 min
17
O
2
inhalation
(B)
3
1
st
measurement
2
nd
measurement
2
1
0
1
2
3
4
5
Rat Number
Fig. 15.7. (
A
) Stacked plots of H
2
17
O spectra from a representative voxel of 3D
17
O
MRSI data acquired before, during and after two consecutive two-min
17
O
2
inhalations
in a rat brain. (
B
) The comparison results between two repeated CMRO
2
measurements
in five rat brains. Adapted from Zhu et al of Ref.
(86)
.
tion of
17
O
2
inhalation, which allows repeated CMRO
2
mea-
surements in the same subject and experimental session (see
Fig. 15.7A
).
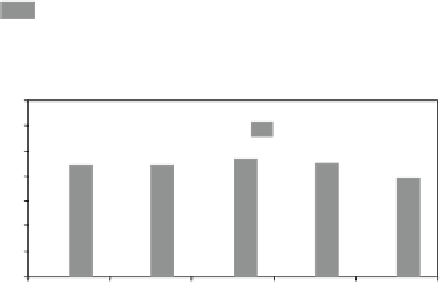
Figure 15.7B
shows the excellent reproducibil-
ity of repeated CMRO
2
measurements in five rats (1st and 2nd
measured CMRO
2
values were 2.26
±
0.18 and 2.20
±
0.14
μ
±
0.05 between the consecu-
tive measurements)
(86)
. The results demonstrate the robustness
and reliability of the simplified in vivo
17
O approach for nonin-
vasively and rapidly imaging CMRO
2
repeatedly in a small brain
of rat. This capability is particularly valuable for studies aiming at
CMRO
2
changes induced by physiological or pathological pertur-
bations in which multiple measurements are required under dif-
ferent conditions (e.g., control versus stimulation for brain func-
tion study). Therefore, the combination of the simplified model
and ultrahigh field in vivo
17
O MRS may potentially provide an
alternative neuroimaging modality for studying the central role of
oxidative metabolism in brain function and neurological diseases
(55, 77)
.
mol/g/min giving a ratio of 1.03
It is well documented that the basal CMRO
2
is sensitive to the
brain temperature (see
(3, 102)
and the references cited therein).
However, most studies reported in the literature were based on
the global CMRO
2
measurements of entire brain using the Kety-
Schmidt method
(92, 93)
, and were limited by the lack of spatial
information regarding regional CMRO
2
. We have conducted a
3.3.3. Demonstration of
in vivo
17
OMRS
Application for Studying
Brain Bioenergetics