Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
natural abundance H
2
17
O signal detected from the rat carotid
blood and
C
a
(t)
measured during a two-minute inhalation of
17
O
2
(54)
. The experimental result showed an approximately lin-
ear relation between the arterial H
2
17
O concentration and the
17
O
2
inhalation time, and the linear fitting of
C
a
(t)
gave the value
of constant
A
required by
Eq. (15.9)
. Note that the
C
a
(t)
(see
Fig. 15.4C
)and
C
b
(t)
(see
Fig. 15.4B
) measurements could
be conducted simultaneously with the configuration of dual
17
O
RF coils and receivers
(97)
.
Finally, the ratio between the decay rates of H
2
17
O signal
measured after the cessation of
17
O
2
inhalation (see
Fig. 15.4B
)
versus that after a H
2
17
O bolus injection (see
Fig. 15.4A
) gives
the constant of
n
, reflecting the H
2
17
O permeability restriction
across the mitochondrial membranes
(54, 87)
.
The values of
C
b
(t)
, CBF and
n
measured from each
17
OMRS
imaging (MRSI) voxel and the value of
A
measured from each
17
O inhalation measurement in the same animal as demonstrated
in
Fig. 15.4
can be used to calculate the absolute CMRO
2
value as a function of inhalation time according to
Eq. 15.9.
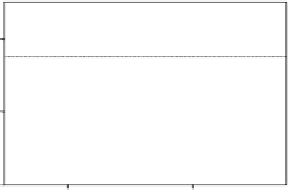
Figure 15.5A
shows one example of CMRO
2
time course from
a representative
17
O MRSI voxel with a temporal resolution of
11 seconds
(54)
. It is evident that the CMRO
2
values are inde-
pendent of
17
O
2
inhalation time if the first two CMRO
2
values
characterized with relatively large fluctuations are excluded. These
CMRO
2
values were averaged for improving measurement accu-
racy. The same procedure and calculation can be applied to all
17
O
MRSI voxels for generating 3D CMRO
2
images in the rat brain
(54, 77)
.
Figure 15.5B
demonstrates three adjacent CMRO
2
images in the coronal orientation from a representative rat brain.
The averaged CMRO
2
and CBF values in the rat brains anes-
thetized with
3.2.4. Imaging CMRO
2
in
Rat Brain
α
-chloralose were 2. 19
±
0. 14
μ
mol/g/min and
0. 53
±
0. 07 ml/g/min (
n
=7), respectively
(54)
.TheCMRO
2
(A)
(B)
4
3
2
1
4.0 mol/g/min
1.0 mol/g/min
0
-1
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
Time (min)
Fig. 15.5. (
A
) Plot of the calculated CMRO
2
values using the complete model as described by
Equation (15.9)
as a
function of
17
O
2
inhalation time. (
B
) Three-dimensional coronal CMRO
2
images of rat brain measured by in vivo
17
O
MRS approach during a two-minute
17
O
2
inhalation. Adapted from Zhu et al of Ref.
(54)
.(
See
Color Plate)