Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
results of optical imaging and electrophysiological measurement
were well correlated not only in their response amplitudes but also
in the spatial location of reduced responses: the border between
normal and reduced response regions in both measurements cor-
responded to the border between normal site and photocoagula-
tion site.
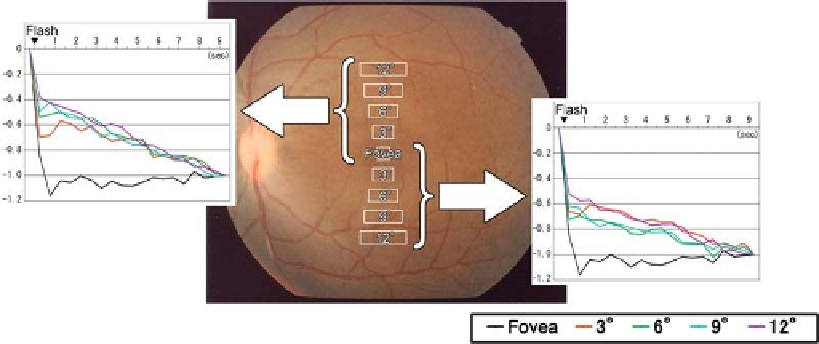
Interestingly, with infrared observation, the time course of
the intrinsic signals evoked by a brief flash stimulus was differ-
ent for different regions of the ocular fundus. Representative
time courses of flash-evoked response at the foveal and peri-
foveal regions under the dark-adapted condition are shown in
Fig. 6.6
. The reflectance changes at the fovea were rapid and
reached a negative peak (darkening) within 100 to 200 ms fol-
lowing the flash. The darkening then gradually returned toward
the pre-stimulus baseline. The signals in the perifoveal regions
(3
◦
-12
◦
) were composed of both fast and slow components. The
time courses of the intrinsic signals of the perifoveal regions were
approximately the same and distinct from the foveal response:
the light reflectance decreased rapidly within 100 ms (flexural
point), and then gradually decreased to reach a trough. The light
reflectance at the fovea did not decrease following the initial neg-
ative peak.
The fovea is a central region (300
m in diameter) in the
posterior retina that is composed of cone photoreceptors and is
free of capillaries and middle or inner layer structures
(26)
.The
perifoveal region has both cone and rod photoreceptors, and its
μ
Fig. 6.6. Time courses of light reflectance changes in a single trial following a diffuse flash, measured at the fovea and
different regions within twelve degrees superior or inferior to the fovea. Amplitudes are indicated as values relative to
the light reflectance changes at the end of each trial (1.0). The four regions tested in each quadrant are indicated as
distances from the fovea (3,6,9 and 12
◦
). (
See
Color Plate)