Hardware Reference
In-Depth Information
These are the three IP address blocks reserved for use on private networks:
•
10.0.0.0
to
10.255.255.255
(Class A network)
•
172.16.0.0
to
172.31.255.255
(Class B network)
•
192.168.0.0
to
192.168.255.255
(Class C network)
The Class C network is the most common range for home routers, with
192.168.1.1
being a typical IP address for the router itself. If you're unsure of the range in use on
your network, you can look at the IP address and route information that was handed
to the Wi-Fi interface by the DHCP service of your router:
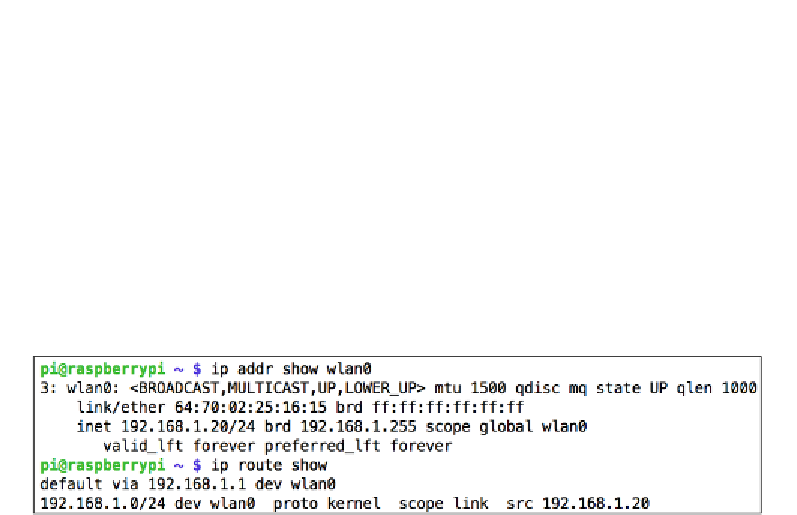
pi@raspberrypi ~ $ ip addr show wlan0
pi@raspberrypi ~ $ ip route show
Wi-Fi interface in the 192.168.1.0/24 address range
The Wi-Fi interface as shown in the previous screenshot has been handed an IP
address in the
192.168.1.0/24
range, which is a shorter way (called
CIDR
notation)
of saying between
192.168.1.0
and
192.168.1.255
. We can also see that the default
gateway for the Wi-Fi interface is
192.168.1.1
. The default gateway is where the
Wi-Fi interface sends all its traffic to talk to the Internet, which is very likely to be the
IP address of your router. So if you find that your interface has been given, for example
10.1.1.20
, the IP addresses of the other computers on your network are most likely
somewhere in the
10.1.1.1
to
10.1.1.254
range. Now that we know what range to
scan, let's see what Nmap can find out about it.