Database Reference
In-Depth Information
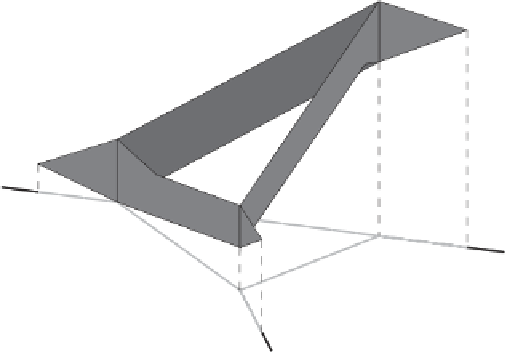
Figure 5.5 A space-time prism on a road network. Note that the possible positions of
moving objects (represented by the cones in Figure
5.3
for unconstrained movement) occur
over the network, and that edges have potentially different speed limits.
to the edges and nodes of the network. In that chapter, map matching algorithms
were classified as geometric, topological, hybrid, and probabilistic. In this sec-
tion we show how the space-time prisms model can be applied to solve this
problem. This method was applied to a real-world case study involving an emer-
gency service in a European city (for privacy reasons we cannot disclose further
information). This service wanted to optimize the time to arrive at the place of
intervention. Even though the company could solve this problem purchasing a
standard route planner, the shortest/fastest route computed by these commercial
route planners would not be the best solution, because, for instance: (1) they do
not take into account the time of the observations (e.g., at five o'clock there is
always a traffic jam at the city station, so cars must avoid this area around that
time, if possible); (2) they do not take into account certain locations, such as
schools; (3) they do not take into account additional information (such as school
routes or tram lines). Thus, they decided to design a tool to solve the problem
described above. As a first step of this work, there was the need to perform
data analysis over a set of routes followed by cars during their interventions.
The officers were asked to record their positions using a GPS device, from the
moment they got a call from the headquarters to the moment when they arrived
at the intervention site. Measures were recorded every ten meters, and drivers
were requested to fill out a survey with questions, for example, about the reason
for taking a particular route. In this scenario, a typical problem that arises is
that about ninety-five percent of the points fall outside the road actually taken.
Thus, there is a need to map points to the road network, that is, a map matching
problem. This problem is formalized in Definition
5.8
.