Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
strated that rule 1 is appropriate in the case of the important prototype Lewis
base H
2
O, given that half the angle between the n-pairs in the n-pair model of
H
2
Oshouldbe
54
◦
(See Fig. 2).
It was not possible to determine experimental PE functions for H
2
O
∼
···
HCl
[113] and H
2
O
ClF [72] in same way. However, another approach was pos-
sible. The energy of each complex was obtained by carrying out a full geom-
etry optimisation at fixed values of the out-of-plane bending coordinate
···
φ
70
◦
. The aug-cc-pVDZ/MP2 level of theory was used and
correction for basis set superposition error was applied. This ab initio po-
tential function was then fitted numerically to the expression of Eq. 1 to give
the coefficients
A
and
B
and thence
a
and
b
.Once
a
and
b
were available,
the matrix of the Hamiltonian
H
=
p
z
/
in the range 0 to
∼
+
V
(
z
) was set up using a basis
composed of 100 harmonic oscillator functions and was diagonalised to give
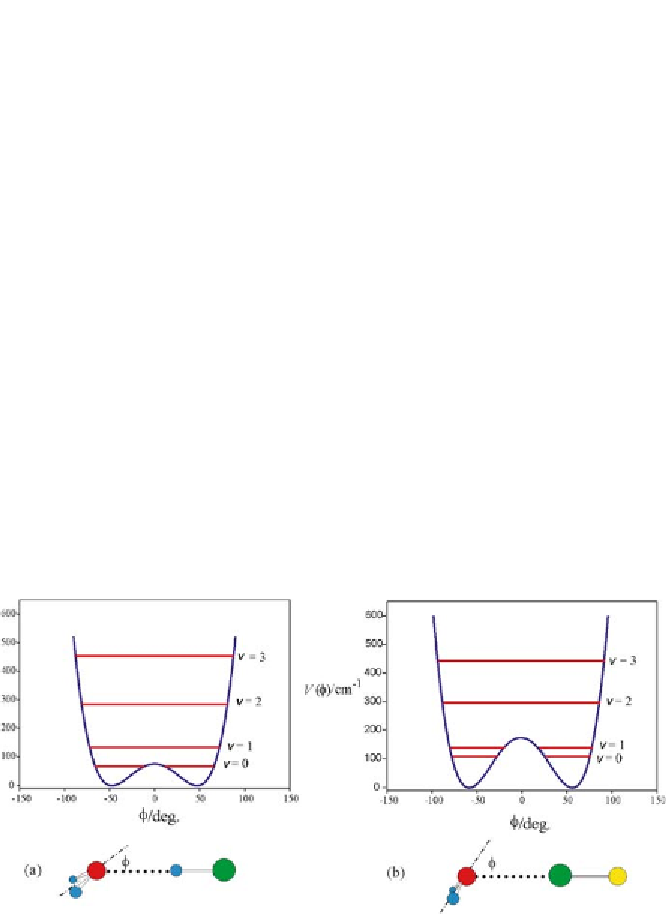
the vibrational energy levels. This approach for H
2
O
2
µ
HF gave values of
φ
min
and the PE barrier height in good agreement with those of the exper-
imentally determined function. Thus we can have some confidence in the
results obtained when the same procedure was applied to H
2
O
···
···
HCl [114]
and H
2
O
and the energy levels are
displayed in Fig. 3. The equilibrium values of the angle
···
ClF [34]; the plots of
V
(
φ
)versus
φ
are 45.7
◦
φ
and
57.4
◦
ClF, respectively, and the two equivalent
minima are separated by PE barriers of
V
0
=80 and 174 cm
-1
, respectively.
These values are similar to the experimental results 46(8)
◦
for H
2
O
···
HCl and H
2
O
···
and 126(70) cm
-1
Fig. 3
The potential energy
V
(
φ
), expressed as a wavenumber, as a function of the angle
φ
for
a
H
2
O
ClF. These have been obtained using ab initio calculations,
by the method discussed in the text. The same approach reproduces the experimen-
tal function of H
2
O
···
HCl and
b
H
2
O
···
···
HF (Fig. 2) very well. Several vibrational energy levels associated
with the motion in
=0 is low
enough that both molecules are effectively planar in the zero-point state, even though the
molecules are pyramidal at equilibrium. See Fig. 1 for key to the colour coding of atoms
φ
are also shown. As for H
2
O
···
HF, the PE barrier at
φ
Search WWH ::

Custom Search