Graphics Programs Reference
In-Depth Information
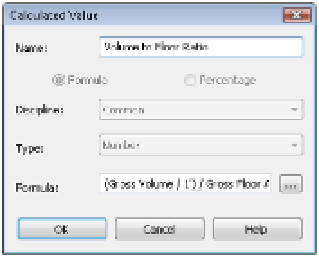
Figure 8.21
create a calculated
value for volume-
to-floor ratio.
b.
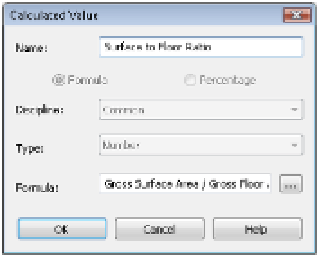
To create your next calculated value, choose the Calculated Value button again and
name this formula
Surface to Floor Ratio
. In the Formula box, enter the following for-
mula, again making sure to maintain the correct case:
Gross Surface Area / Gross Floor
Area
. Once you've entered the formula, click OK (Figure 8.22).
Figure 8.22
create a calculated
value for the
surface-to-floor
ratio.
c.
The finished schedule is shown in Figure 8.23. Notice that, proportionally, a sphere
and a cube have efficient floor areas compared to their corresponding surface area and
volume.
Figure 8.23
completed schedule
On the other hand, the pyramid mass will require significantly more surface and volume
to create the same relative surface area as a cube or a sphere; thus, a pyramid takes far more
surface area than a cube to contain the same space. Perhaps this is why pyramids aren't a
common building mass—they're too expensive.
You can download the inished ile from the topic's companion website,
www.sybex.com/
go/MasteringRevit2015
. It's in the Chapter 8 folder and is named c08-Massing-1-
Finished.rvt.