Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
P Pa a
=
(
).
≥
[5.46]
f
a
cr
It can be seen that this equation is the case described in sections 3.3.1
and 3.3.3.
If there are no defects in the structure, then the term associated with
the size of the defect is removed from equation [5.43]. For example, the
following equation is obtained for the probability of failure of a defect-free
strcucture with the strength criterion of the material in the form of yield
stress σ
T
and random static load, characterised by stress σ:
s
s
Tmax
T
( )
[5.47]
∫
∫
P
= ρ s
()
ρs ss
dd
,
d
s
T
s
T
T
s
s
Tmin
min
It can be seen that in this case the model proposed by A.R. Rzhanitsyn
(section 3.1) is described.
5.3.6 Comparison of results of calculations using
procedures described in sections 5.3.5 and 3.1
Software PN1.1
96
(a brief description is given in the appendix) was
developed for calculations using the generalised method (section 5.3.5).
The software was used for calculated on the basis of an example for the
calculation of steel structures using the method proposed by Rzhanitsyn
(see section 3.1). The calculations yielded the probabilities of fracture for
the input data from the example given by Rzhanitsyn (Fig. 5.51):
Calculation No. 1:
2
s=
2663 kg/cm
266.3 MPa
=
- Average expected yield stress;
T
2
D
s
=
284 kg/cm
=
28.4 MPa
- Standard deviation of yield stress;
T
s
=
1400 kg/cm
2
=
140 MPa
- Average value of stress;
- Standard deviation of stress;
D
s
=
140 kg/cm
2
=
14 MPa
Calculation No. 2:
2
- Average expected yield stress;
s
=
2663 kg/cm
=
266.3 MPa
T
D
s
=
284 kg/cm
2
28.4 MPa
=
- Standard deviation of the yield stress;
T
2
- Average value of stress;
s
=
1600 kg/cm
=
160 MPa
2
D
s
= =
- Standard deviation of stress.
The results of the calculations show that at the allowable stress in
the structure of [σ] =1400 the failure probability is
P
f
= 3.3·10
-5
, and at
[σ] = 1600 the probability of failure
P
f
= 5.5·10
-4
and 4.7·10
-4
, close to
the probability values, obtained by the Rzhanitsyn' method (3.2·10
-5
and
4.7· 10
-4
, respectively).
It is also necessary to mention another result which follows from the
numerical solution of the Rzhanitsyn's problem. The range of the stress
160 kg/cm
16 MPa
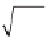






Search WWH ::

Custom Search