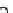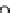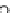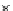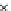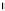Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
6.5
Model
Rater
6
5.5
5
4.5
4
3.5
3
2.5
2
0
5
10
Landmark Index
15
20
Figure 17.
Comparison of the magnitude of deformations of landmarks predicted by the
model and the rater for the HC tumor case.
occurs at
υ
∈
[0
.
475
,
0
.
499], which is in agreement with the almost-incompressible
behavior reported in the brain biomechanics literature. Therefore, in subsequent
simulations, we adopted the value
υ
=0
.
485 — near the middle of this range.
4.3.7.5. ValidationExperiments
With
υ
=0
.
485 and the values of
e
determined
above, the optimal value of
P
for each tumor case was recorded. These values of
P
and
e
and the corresponding residual errors in the model predictions are reported
in Table 2. Statistics on the errors and landmark deformations are also reported in
the same table.
In Figure 17 we compare the magnitude of the landmark deformations for
the HC case predicted by the model to those found by a rater. For most of the
landmark points, the model seems to be underestimating the magnitude of the defor-
For this case, the smallest percentage residual error compared to the
mation.
rater's magnitude of deformation (landmark point 6) and was equal to 15.31%.
The deformation of that landmark point as predicted by the rater was 4.15 mm.
On average, the model is able to predict more than 62% of the deformation for HC.
Since the coordinates of the landmarks were treated as ground truth, quan-
tification of the accuracy of the rater's placement of these landmark points in the