Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
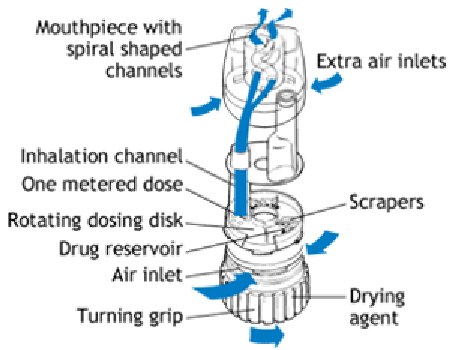
An example of multi-dose reservoir inhalers is the Turbuhaler
®
(Astra
Zeneca) (Figure 7) which contains up to 200 doses of micronized drug stored
in a reservoir which releases the powder to a rotating disc having holes filled
with the powder. A metered dose is introduced to the inhalation channel when
the rotating disc is clicked by twisting it back and forth.
(Source:
www.asthma)
.
Figure 7. Design of the Turbuhaler
®
device. This consists of a reservoir containing up
to 200 doses of the powdered drug, and a perforated rotating disc through which the
drug passes for inhalation upon actuation.
3.3. Medical Nebulizers
Medical nebulizers are inhalation devices capable of delivering large
volumes of aerosols from aqueous formulations without the need for further
processing as in case of pMDIs or DPIs. The properties of the aerosols
generated from nebulizers are highly dependent on its operating principle and
the design of the nebulizer as well as the formulation physicochemical
properties, such as viscosity and surface tension. There are three types of
medical nebulizers: air-jet, ultrasonic and the recently commercialized
vibrating-mesh nebulizers.
3.3.1. Air-Jet Nebulizers
Air-jet nebulizers are also known as jet, pneumatic, or compressor
nebulizers. Sometimes air-jet nebulizers are referred to as ―venturi‖ nebulizers.