Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
where P
o
is atmospheric pressure, A is the cross-sectional area of the ball, and
m is the mass of the ball. They define a characteristic length, λ, as
m
(2)
A
where ρ is air density. The resulting expression for velocity as a function of
distance down the tube is then
x
2
(3)
v
(
x
)
v
1
max
x
x
where
P
(4)
v
a
o
max
0
The ball is 40mm in diameter, so that A=0.0012566 m
2
. Nominally,
P
o
=101,300 Pa and ρ=1.225 kg/m
3
,
so v
max
= 287.6 m/sec. Finally, a typical
ball weighs approximately 2.3g. The resulting predicted velocity profile along
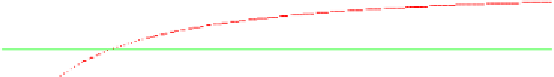
the barrel is show in Figure 22.
300
200
100
0
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
2.5
3
Distance (m)
Reproduced with permission. Copyright retained by Inderscience Publishers.
Figure 22. Predicted Velocity Along the Barrel Using the Analytical Model.
Note, that the predicted velocity asymptotically approaches a maximum of
approximately 287 m/sec. This is due to the increasing mass of air behind the
ball that must be accelerated to the speed of the ball as it moves along the