Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
T
SH
2
−
1
T
SH
1
R
1
y
det
J
<0
(orientation
reversing)
T
(
R
1
)
T
(
R
2
)
y
'
R
2
T
−
1
LC
−
1
Z
Z
2
0
U
−
det
J
>0
(orientation
preserving)
U
R
R
1,1
LC
x
x
'
(a)
(b)
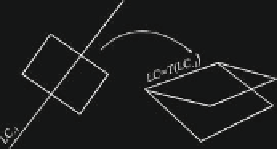
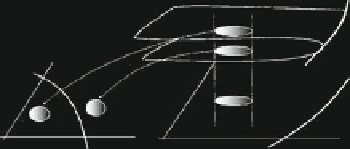
Fig. C.3
(
a
) A qualitative visualization of a map of the plane, and how the folding relates to the
sign of the Jacobian matrix. (
b
) Visualizing a Riemann foliation of the plane, in the case of a
Z
0
Z
2
noninvertible map
@T
1
=@x
1
@T
1
=@x
2
@T
2
=@x
1
@T
2
=@x
2
:
J
.
p
/
D
(C.4)
A qualitative visualization is given in Figs. C.3a, b. Of course, if the map is continu-
ously differentiable then the change of the sign of
det
.
J
/ occurs along points where
det
.
J
/ vanishes, thus giving the characterization of the fold line LC
1
as the locus
where the Jacobian vanishes.
In order to give a geometrical interpretation of the action of a multi-valued
inverse relation T
1
, it is useful to consider a region Z
k
as the superposition of
k sheets, each associated with a different inverse. Such a representation is known as
Riemann foliation
of the plane (see for example Mira et al. (1996)). Different sheets
are connected by folds joining two sheets, and the projections of such folds on the
phase plane are arcs of LC. This is shown in the qualitative sketch of Fig. C.3b,
where the case of a Z
0
Z
2
noninvertible map is considered. This graphical rep-
resentation of the unfolding action of the inverses also gives an intuitive idea of the
mechanism which causes the creation of disconnected basins for noninvertible maps
of the plane.
To give an example, let us again consider a quadratic map T
W
.x;y/
!
.x
0
;y
0
/,
extensively studied in Mira et al. (1996) and Abraham et al. (1997), defined by
x
0
D
ax
C
y;
y
0
D
b
C
x
2
:
T
W
(C.5)
Given x
0
and y
0
, if we try to solve the algebraic system with respect to the unknowns
x and y we get two solutions, given by
x
D
p
y
0
b;
x
D
p
y
0
b;
T
1
1
y
D
x
0
C
a
p
y
0
b;
;
T
1
2
y
D
x
0
a
p
y
0
b;
W
W
(C.6)
if y
0
b, and no solutions if y
0
<b.So,(C.5)isaZ
0
Z
2
noninvertible map,
where Z
0
(the region whose points have no preimages) is the half plane Z
0
D
f
.x;y/
j
y<b
g
and Z
2
(region whose points have two distinct rank-1 preimages)



Search WWH ::

Custom Search