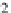Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Fig. 4.6.
Simulated ECG signals (leads I and V4) obtained using heart-torso full coupling (black)
and uncoupling (red)
heterogeneity, the repolarization and depolarization waves travel in the same direc-
tion, which leads to the discordant polarity, between the QRS- and the T-waves,
observed in lead I. On the contrary, unipolar leads (aVR, V1 and V4) present a sim-
ilar polarity, irrespective of the ADP heterogeneity (see also [16]). As a result, as
also noticed in [7, 33, 50, 51], transmural APD heterogeneity is a major ingredient
in the simulation of a complete 12-lead ECG with physiological T-wave polarities.
Heart-torso uncoupling
Concerning the heart-torso uncoupling approximation (4.9), the comparison reported
in Fig. 4.6 shows that heart-torso uncoupling compromises the accuracy of the ECG
signals (notice the difference of amplitudes). Therefore uncoupling cannot be rec-
ommended in general, although it can be a reasonable choice to get qualitatively
correct ECGs.
Monodomain approximation
Let us notice that, without the uncoupling assumption (4.9), approximation (4.6)
becomes
div
σ∇
V
m
=
χ
m
∂
t
V
m
+
I
ion
(
V
m
,
w
)
−
I
app
,
in
Ω
H
,
(4.17)
σ∇
V
m
·
n
=
−
μσ
e
∇
u
e
·
n
,
on
Σ
,
where
is a dimensionless parameter related to the local conductivities (see
also [14]). Thus, we cannot derive anymore the usual monodomain model since the
unknowns
V
m
and
u
e
are still coupled. In that case, solving this system does not
reduce the computational complexity, compared to (4.8).
It seems more interesting, in terms of computational cost, to combine the mon-
odomain approximation with the heart-torso uncoupling approximation (see, e.g.
[30, 50]). Indeed, this yields a simplified mathematical model which allows a fully
decoupled computation of
V
m
,
u
e
(which is equal to
V
m
up to a multiplicative con-
stant) and
u
T
. In that case, the ECGs obtained are very similar to the ECGs obtained
for the bidomain model combined with the heart-torso uncoupling hypothesis.
μ
∈
(
0
,
1
)