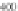Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
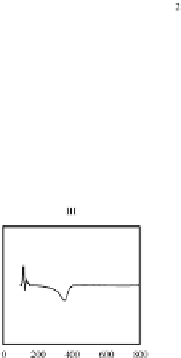
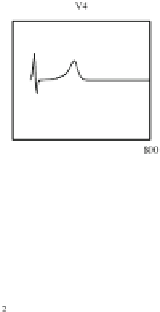
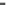
Fig. 4.5.
Simulated normal 12-lead ECG signals
Numerical simulations have also been carried out for some pathological condi-
tions like left or right bundle branch blocks (see [7] or [72] for details). The numerical
ECG signals satisfy the typical criteria used by medical doctors to detect the patho-
logy, and this without any recalibration of the model's parameters besides the natural
modifications needed to model the disease (i.e. delayed activation in the right or left
ventricle). This suggests that the ECG simulator has some predictive features.
Remark 3.
We refer to [12, 21] for two examples of how the ECG simulator devel-
oped can be used in different contexts and applications.
4.4.3 Impact of some modelling assumptions
The ECG simulator can be used to investigate numerically the impact of some mod-
elling aspects. To test alternative modelling hypotheses, we will compare the ECG
to the one obtained in a reference simulation, denoted by
RS
, corresponding to the
healthy case described in the previous paragraph.
Cell heterogeneity
As mentioned at the beginning of Sect. 4.4, a heterogeneous coefficient
close
has
been considered in the
RS
to incorporate an APD gradient across the left ventricle's
transmural direction. To reduce the complexity of the model, it may be tempting to
take a constant coefficient. But it has been observed that this simplification would
affect the polarity of the T-wave in lead I (see [7]). Indeed, without transmural APD
τ