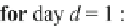Civil Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
4 Simulation Results
The described methodologies and algorithms have been implemented for simu-
lation in a Java application developed by the authors and described in Virote and
Neves-Silva (
2010
), Virote (
2010
). Compared with approach described in Fig.
7
,
the building has been replaced by a simulator based on multi-agent system
approach and a rule-based reasoning engine (Virote
2010
). The objective is to use
this simulator as a data generator capable of reproducing the same occupancy
patterns as a real building. This is achieved by controlling the behaviour of the
occupants with the occupant behavioural model described in
Sect. 1
. The occu-
pants are implemented in each software agent in which the occupant behavioural
model is integrated.
The objective of the simulations is to predict the building energy consumption
and analyse the spaces occupancy patterns. Furthermore, the opportunity of
improving the energy consumption is discussed. Changing the occupant behav-
ioural model parameters within the building simulation is expected to have a direct
impact in the overall building energy consumption resulting in more or less wasted
energy. This must be reflected in the ECM predictions.
The purpose of the ECM is to capture the space occupancy patterns in order to
reproduce them. This result is verified in the simulation depicted in Fig.
10
, which
was performed in building A composed by 10 spaces. The ECM predictions are
achieved by the calculation of the stationary state distribution as they are only
dependent on the model parameters. The outcome is that the model can reliably
capture and reproduce the space occupancy patterns.