Civil Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
R
k
R
k
XP
¼
IX
,
P
I
ð
Þ
X
¼
0
,
RX
¼
0
,
P
¼
ð
6
Þ
where R represents the null space basis of X and the steady-state vector P is the
result of the normalisation of R.
The measurements are divided into two clusters, one for estimation and the
other for validation. This process consists of dividing the spectrum of each space
and using half of the observation period data for the model parameters estimation
and the other half for parameters optimising by finding one optimal path. That is,
which time series best describes the space? Since ECM is a stochastic model,
every time the ECM is simulated a different state sequence is produced, and
consequently, different occupancy patterns and energy consumptions are pre-
dicted. This property could be interesting for some applications, although it is not
suitable for prediction and decision support. To overcome this limitation, a method
to start the model sequence is applied.
One important aspect of computation is that, usually, for dealing with random
numbers, a pseudo-random number generator (PNGR) is used. This applies an
algorithm for generating a sequence of numbers that approximates the properties
of random numbers. A characteristic of this algorithm is that a PNGR can be
started from an arbitrary starting number called seed, and it will always produce
the same sequence as long as initialised with the same value. So to achieve a
random number generator, the key is to use different seed values. As a final
remark, this allows a stochastic model to behave like a deterministic process. Each
time the stochastic model is simulated with the same seed, and it will always
behave likewise. To account for this, the method of selecting a seed is important.
To select a seed for the ECM state sequence generation, two algorithms have
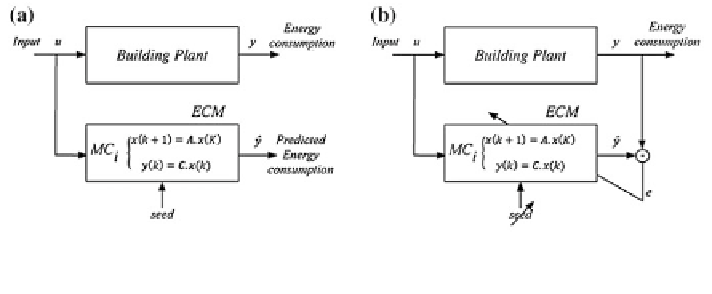
been developed: static and dynamic algorithm. The block structure of these
algorithms is depicted in Fig.
9
. The first algorithm attributes a seed to each MC in
the ECM based on the model parameters
Fig. 9
Block
diagrams
illustrating
the
seed
discover
algorithms.
a
Static
algorithm,
and
b dynamic algorithm