Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
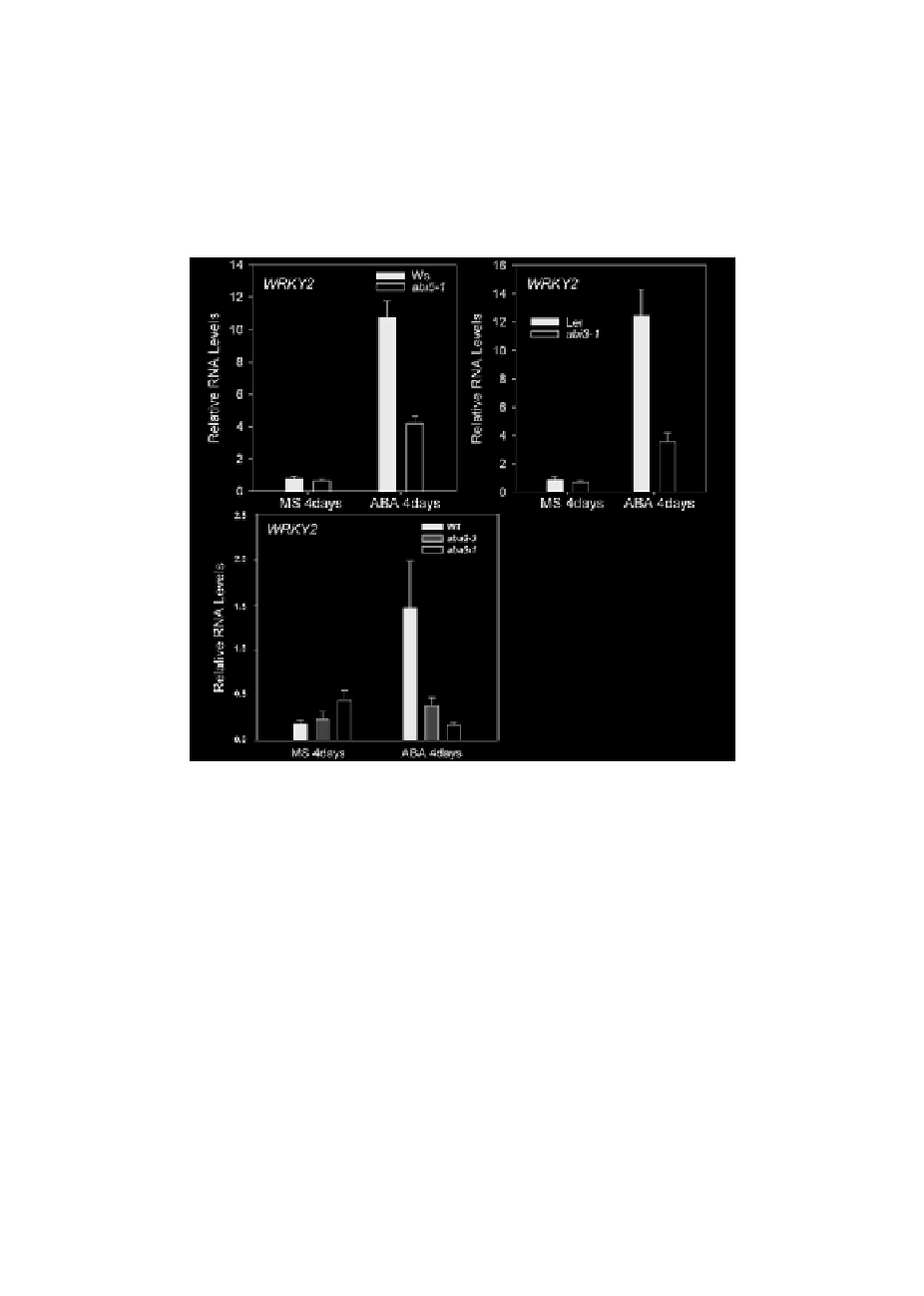
quantitative RT-PCR with gene-specific primers. In the absence of ABA, the ex-
pression level of WRKY2 in the wild type (Ws) was 1.2 times of that in the abi5-1
mutants. In the presence of ABA, the level of WRKY2 was 2.5-fold. On the other
hand, ABA treatment led to 13.6-fold increase in accumulation of WRKY2 in the
wild type and 6.5-fold increase in abi5-1 mutants (Figure 7). These results suggest
ABI5 is an important regulator of ABA-induced WRKY2 expression.
Figure 7.
RNA levels of WRKY2 in abi5-1, abi3-1, aba2-3 and aba3-1 mutants.
RNA was extracted from seedlings on MS medium without ABA or with 1.5
µ
M ABA 4 d post-stratification.
Relative RNA levels of WRKY2 were analyzed using gene-specific primers by real-time PCR. Three independent
experiments are shown by reextracting RNA from other samples. Each experiment also was executed three
times.
Without ABA, the level of WRKY2 in the wild type (Ler) was 1.2-fold higher
than that in abi3-1 mutant. In the presence of ABA, the WRKY2 transcript level
in wild type was 3.5-fold higher than that in abi3-1 mutant (Figure 7). These
results indicate ABI3 maybe is a positive regulator of ABA-induced WRKY2.
We also examined the expression level of WRKY2 in ABA-deficient aba2-3 and
aba3-1 mutants [43,44]. As shown in Figure 7, with ABA, the expression level of
WRKY2 in the wild type was 7.5 time higher than that without ABA, but the
expression levels of WRKY2 in aba2-3 and aba3-1 mutants were only 1.6 and
0.38 times of those without ABA, respectively. On the other hands, without ABA,
the expression levels of WRKY2 in aba2-3 and aba3-1 mutants were 1.2 and 2.3