Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
20
20
MMS(K=5)
sMDIST(K=5)
Random(K=5)
GMMS(K=5)
sMDIST(K=5)
Random(K=5)
18
18
16
16
14
14
12
12
10
10
8
8
6
6
4
4
2
2
0
0
-2
-1
0
1
-2
-1
0
1
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
False Accept Rate (%)
False Accept Rate (%)
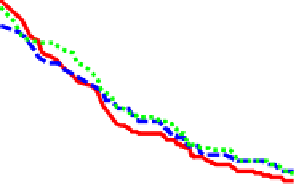
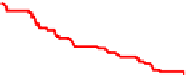
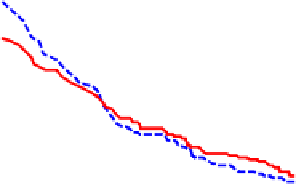
Fig. 9.
ROC curves show comparison between
MMS , sMDIST and Random when K=5
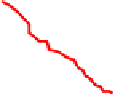
Fig. 10.
ROCs show comparison between
GMMS, sMDIST and Random when K=5
20
20
MMS(K=2)
GMMS(K=2)
MMS(K=3)
GMMS(K=3)
MMS(K=4)
GMMS(K=4)
MMS(K=5)
GMMS(K=5)
18
18
16
16
14
14
12
12
10
10
8
8
6
6
4
4
2
2
0
0
10
-2
10
-1
10
0
10
1
10
-2
10
-1
10
0
10
1
False Accept Rate (%)
False Accept Rate (%)
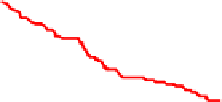
Fig. 11.
ROCs show comparison between
MMS and GMMS when K=2,3
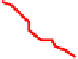
Fig. 12.
ROCs show comparison between
MMS and GMMS when K=4,5
From Figure 11 and Figure 12, we can find the facts that when FAR below a special
threshold GMMS is better than MMS and when FAR above the threshold MMS is bet-
ter than GMMS. Although it is the optimized method according to the maximized score
model, MMS is not always better than GMMS. The reason may be that N=8 is not large
enough and N-K can not represent the set T
N
+
effectively. In addition, consider each
biometric trait as one class, the maximized score model makes the intra-class distance
smaller and at the same time may make the inter-class distance smaller too.
6.2 Experiment for Template Update
When we conduct experiment for template update, we first choose 4 templates as the
template group. Then the next four samples are used for template update. For ONLINE
strategy, we conduct template update procedure four times. Each time, we choose four
templates from the original four templates and the newly added samples. So the tem-
plate update procedure is based on the template selection procedure. For OFFLINE
strategy, we conduct template update procedure only one time. This procedure is the




























































































































































































































































































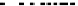






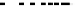







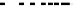



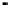





































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search