Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
API
MeOH/H
2
O conditions
0.5% impurity
10
20
Retention Time (min)
API
THF/H
2
O conditions
0.5% impurity
0.3% impurity
10
20
Retention Time (min)
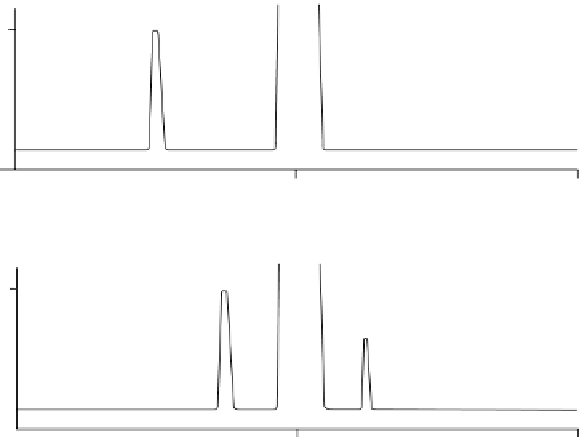
FIgure 7.3
Hypothetical example: Improved resolution achieved by changing mobile
phase selectivity.
change in pH are the equivalent of a 20% change in the organic solvent composition,
and are often underutilized.
Another valuable, yet traditional approach to manipulating method specificity
utilizes methods with alternate or orthogonal selectivity, as illustrated in Figure 7.3.
In this example, the preferred analytical method is 20 min long, and utilizes an
isocratic elution of a C
18
HPLC column with 50/50 MeOH/H
2
O. However, only one
impurity (0.5%) is observed by this method, and it elutes at a retention time of 5
min, while the API elutes at a retention time of 10 min, and accounts for 99.5% of
the integrated chromatogram peak area; no other impurities are observed, and all
impurities elute within the run time. To determine if any impurities are co-eluting
with the API, the method selectivity was then changed. Changing the elution condi-
tions from 50/50 MeOH/H
2
O to 30/70 THF/H
2
O, the API peak still elutes at 10 min
retention time, but the 0.5% impurity now shifts to 7.5 min, and a new impurity,
present at a level of 0.3%, is observed at 12.5 min. Furthermore, the API peak now
only represents 99.2% of the integrated chromatogram peak area. This strongly sug-
gests that the 0.3% impurity co-eluted with the API peak when using the H
2
O/MeOH
conditions. If the 0.3% impurity was an API stereoisomer with the same mass spec-
trometric fragmentation pattern, then this approach, while traditional, would have
been the best one to use to solve this problem.
Other approaches to changing selectivity include changing columns, using
different modes of HPLC (e.g., hydrophilic interaction chromatography, or HILIC),
or employing entirely different techniques orthogonal to HPLC, such as capillary
electrophoretic techniques, gas chromatography, and thin layer chromatography.