Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
120
100
80
*
*
*
#
60
40
20
0
TOCP (mM)
Taurine (mM)
0
0
1
0
1
1
1
3
1
9
Fig. 22.1
Effects of taurine on the viability of C6 glioma cells exposed to TOCP. C6 glioma cells
were treated with 0, 1, 3, and 9 mM of taurine for 30 min followed by exposure to 1 mM TOCP for
48 h. Cell viability was measured by MTT assay. Data are shown as mean ± S.D. from three sepa-
rate experiments; the symbol (#),
P
< 0.05 as compared with control; the symbol (*)
P
< 0.05 as
compared with TOCP exposure alone
normal C6 glioma cells had clear edges and nucleus. Exposed to TOCP, C6
glioma cells displayed obvious cell body shrinkage, nuclear condensation, and
loss in cell membrane integrity (Fig.
22.3
). The addition of taurine, however,
dramatically prevented cell morphological deterioration. Most of C6 glioma
cells showed normal cell morphology with normal nuclear size and integrity
(Fig.
22.3
).
22.3.4
Effects of Taurine Pretreatment on the Content
of GSH and the Activity of GPx
The average GSH content was 8.6 ± 1.0 mg/g protein, and the activity of GPx was
78.6 ± 4.9 U/mg protein in C6 glioma cells, respectively. After exposure to 1 mM
TOCP, C6 glioma cells antioxidant system was disturbed, namely, the content of
GSH and the activity GPx decreased (Fig.
22.4
). Pretreatment with taurine
significantly prevented the depletion of GSH (Fig.
22.4a
) and preserved the activity
of GPx (Fig.
22.4b
).

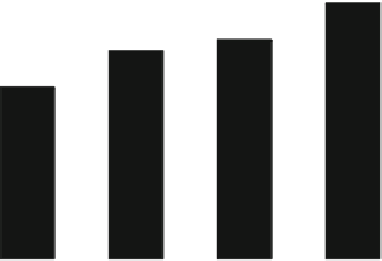





































Search WWH ::

Custom Search