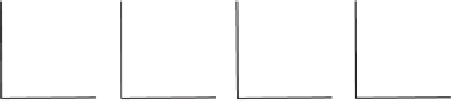Database Reference
In-Depth Information
stock
prices
air
temperatures
sea
temperatures
wind
speeds
EEG
1
1
1
1
1
80%
comp.
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
0
1
1
1
1
correlation: .98
correlation: .93
correlation: .95
correlation: .90
correlation: .92
1
1
1
1
1
90%
comp.
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
0
1
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
correlation: .96
correlation: .76
correlation: .86
correlation: .74
correlation: .68
1
1
1
1
1
95%
comp.
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
correlation: .93
correlation: .57
correlation: .76
correlation: .70
correlation: .58
Fig. 6. Correlation between the peak similarity of original series and the peak similarity
of their compressed versions. We show the correlation for three compression rates: 80%,
90%, and 95%.
vl
value of the left important point of the leg
vr
value of the right important point of the leg
il
index of the left important point
ir
index of the right important point
ratio
ratio of the endpoints, defined as
vr/vl
length
length of the leg, defined as
ir-il
Fig. 7.
Basic data for a leg.
length
p
/D
and
length
p
· D,
where
C
and
D
are parameters for controlling
the search.
We index all legs in the database by their ratio and length using a
range
tree,
which is a standard structure for indexing points by two co-ordinates
[Edelsbrunner (1981), Samet (1990)]. If the total number of legs is
l,
and
the number of retrieved legs with an appropriate ratio and length is
k,
then
the retrieval time is
O
(
k
+lg
l
).