Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
compaction can be described thus:
Excess voidage, %
with air void determination, this is performed on finely
ground concrete slice specimens (see
184
) that must be
large enough to represent adequately the concrete
element from which it is taken (typically 100 × 100 mm
minimum area). The normal methods involve either
linear traverse or point-counting determinations to
establish the volume proportions of coarse aggregate,
fine aggregate, cement paste, and air voids. As with
Compaction
>0.5
Very good
>0.5-3.0
Good (normal for satisfactory
quality structural concrete)
>3.0-5.0
Medium
>5.0-10.0
Poor
>10.0
Very poor
In addition, the term 'honeycombed' is used to describe
interconnecting large entrapped air voids (excess voidage
may be as high as 30% locally) arising from inadequate
concrete compaction or a lack of mortar (binder and fine
aggregate).
For accurate determination of the air void system, it is
necessary to undertake manual point-counting or linear
traverse measurements of finely ground concrete slice
specimens. In Europe, determination of air void content
of hardened concrete is performed in accordance with EN
480: Part 11 (British Standards Institution, 2005) and in
America, ASTM C457 (ASTM International, 2008c) is
used. It is important to ensure that the sample is
adequately representative of the concrete. The minimum
area of concrete slice for concrete with a 20 mm coarse
aggregate would be 10,000 mm
2
(and greater for concrete
with larger aggregate). The finely ground slice specimen
is carefully prepared, ensuring a scratch-free surface with
well defined air void edges. The volume proportions of
aggregate, cement matrix, entrapped air voids, and
entrained air voids are determined by examining the slice
using a low-power binocular microscope with the aid of
an oblique incident light source and a mechanical stage.
The air void content is then calculated using formulae
supplied in the EN or ASTM standards.
The manual method of air void analysis takes several
hours to perform for each specimen. With this in mind,
an automated apparatus, the RapidAir 457 has been
developed to perform ASTM C457 or EN 480-11 air void
analysis in less than 15 minutes (Jakobsen
et al
., 2005).
The apparatus comprises a computerized control unit
(and monitor) with image analysis software, a video
camera, and a microscope objective mounted on a
moving stage (
186
). The concrete sample preparation for
image analysis is similar to that required for the manual
method, except that the contrast between the air voids
and the concrete has to be enhanced by colouring (
187
).
186
186
The RapidAir 457, Automated Air Void Analyzer
system. (Courtesy of Concrete Experts International.)
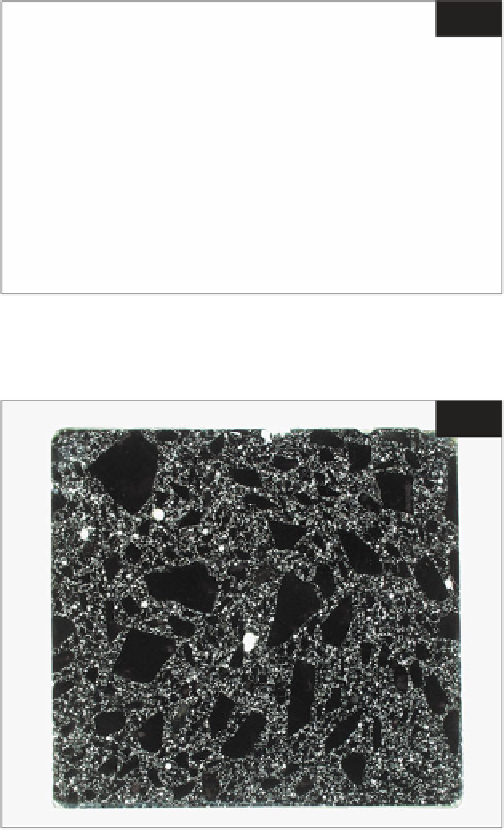
187
187
Surface of an approximately 100 × 100 mm finely
ground slice of air-entrained concrete after contrast
enhancement, to allow air void analysis using the
RapidAir 457. Entrapped and entrained air voids
appear white against the black background of
aggregate and cement matrix. (Courtesy of Concrete
Experts International.)
M
ODAL ANALYSIS OF CONCRETE BY PETROGRAPHIC
PROCEDURES
Modal analysis of hardened concrete (also known as
'micrometric' analysis) may be used to determine binder
content, aggregate content, and aggregate grading. As