Civil Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
5
Do = 670.6 mm
W
S. + FE d=11. 9 mm
W
−
S. + FE d=16. 3 mm
W
−
4
S. + FE d=23. 7 mm 8 Li .
W
−
S. + FE d=24. 1 mm
W
−
−
q
max
q
o
S. + FE d=26. 1 mm
W
S. + FE d=26. 6 mm
W
−
S. + FE d=27. 8 mm
W
−
3
−
S. + SE d=24. 1 mm
W
S. + SE d=26. 6 mm
W
−
S. + SE d=27. 4 mm
W
−
−
S. + SE d=27. 7 mm
S. + SE d=24. 2 mm
2
1
5
10
20
200
50
100
N/mm
2
1000
specific tensile force S/d
2
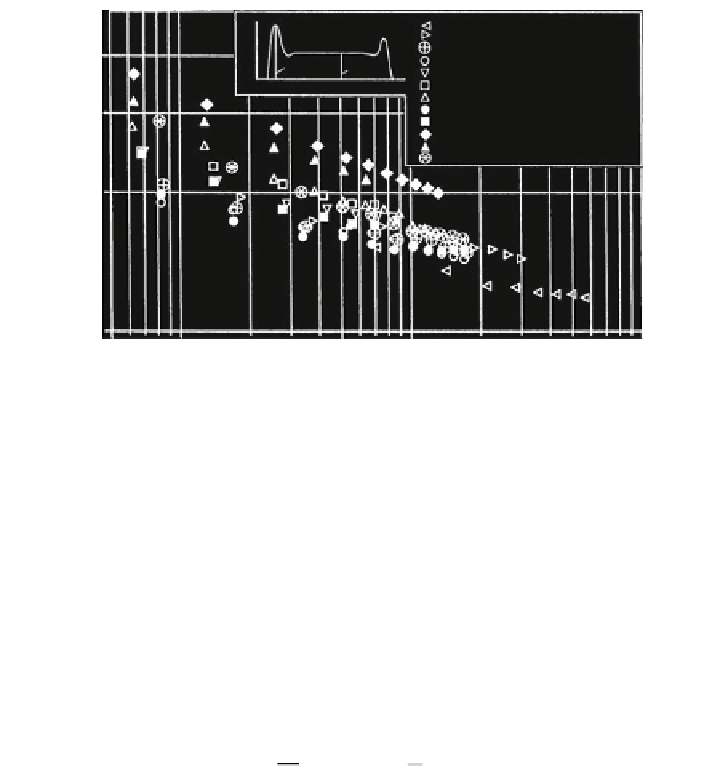
Fig. 3.20
Maximum relative line pressure qmax/qo, Häberle (
1995
)
The specific tensile force S/d
2
is to be taken in N/mm
2
. The standard deviation
is lg s = 0.050.
Häberle (
1995
) also evaluated the difference of the sheave winding angle
D
#
= D
#
1
+ D
#
2
between the run on and run off angle for limp-bending yarn and
the angle of the line pressure peaks for wire ropes (D
#
1
and D
#
2
correspond with
#
0
in case of tape). In Fig.
3.21
, the evaluated winding angle difference is only
shown for specific tensile force S/d
2
= 68.3 N/mm
2
(The results with specific
tensile forces S/d
2
= 30 and 300 N/mm
2
as points have not been shown here).
From the regression calculation for the Warrington-Seale ropes 6 9 36 sZ with
fibre or steel core used for the tests, the winding angle difference is
d
2
1
:
073
lg
D
S
S
d
2
lg
D
lg D
#
¼ 2
:
870
0
:
383
lg
d
þ
0
:
171
lg
d
:
ð
3
:
29
Þ
The winding angle difference D
#
is given in degree and the specific tensile
force has to be taken in N/mm
2
. The standard deviation is lg s = 0. 0337.
The influence of the line pressure peak is shown very impressively by the
number of bending cycles which a wire rope attains with different deflection
angles. Müller (
1961
,
1966
) carried out such endurance tests. As one of his test
results the number of bending cycles of a wire rope as a function of the deflection
angle is given in Fig.
3.53
, Sect.
3.2.3
. The smallest number of bending cycles
from this figure exists for the deflection angle
#
D,dip
= 20.
At this angle, the pressure peaks of the running on and the running off sides of
the wire rope work together. Furthermore, in this range the free bending radius of
the wire rope bow is the same as that of the sheave radius which means that all the
rope bending stresses work together with the pressure to their full extent. This
deflection angle
#
D,dip
= 20 from Müller's diagram, which is given for a specific

Search WWH ::

Custom Search