Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
description and discussion on computing the transition probabilities is
found in Keane (1993: pp. 550-554).
Our application has three choice alternatives (technologies).
Because the choices are mutually exclusive, two binary indicators are
sufficient in identifying them. These two binary indicators are defined as
follows.
if traditional heating with storage is chosen
0,
otherwise
if co-generator with storage is chosen
0,
otherwise.
The third choice of traditional heating without storage is observed
if
The log likelihood function,
for a single observation has the
form
where are the simulated probabilities, conditional on all choices made
before time a set of exogenous instruments and trial
parameters The set of instruments
X
includes the price of energy,
capital stock in structures, capital stock in energy installations, labour, and
the size of the operation. These instruments were used in logarithmic
forms. Also, dummy variables identifying the vegetable firms and cut
flower firms were included in the set of instruments. The GHK simulator
was based on 20 draws for the error sequence of each firm (
i.e., S
=20).
This number of draws has been found to result only in a negligible
simulation bias even when the simulated choice probabilities are small
(Börsch-Supan and Hajivassiliou 1993).
The lower-triangular matrices, consisting of the elements that are
used in multiplying the simulated error sequences in the choice
equations (for and are denoted by and In order to
decrease the parameter space and identify the parameters in the model, a
set of restrictions was imposed on the elements of and All off-
diagonal elements were imposed to zero, except for the elements in the first
column. Furthermore, the upper most diagonal element in both
A's
was set
equal to one implying that
(as in standard Probit
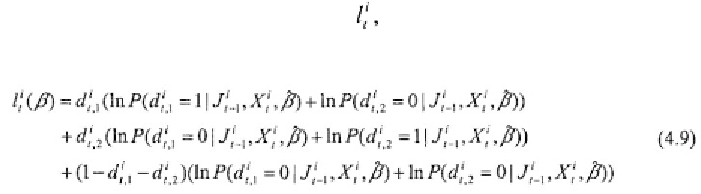
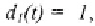
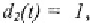


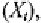


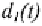
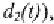


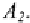

Search WWH ::

Custom Search