Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
ligand (100%
ee
), while the (
P
)-[Yb
L
RRRRRR
]
3þ
isomer is a thermodynamic product
(90%
ee
). In addition to the thermodynamic control over the absolute helicity, the inver-
sion process is dependent also on the size of the Ln
3þ
ion, for example, it is observed for
solutions of the [Tb
L
]
3þ
complex, but not for [Eu
L
]
3þ
.
11.3 Folded Oligomers in Which Metal Coordination Nucleates the
Formation of an Abiotic Single-Stranded Helix
Nucleation of a stable three-dimensional structure by metal coordination requires
careful design of biomimetic oligomers capable of non-covalent interactions upon
metal binding. Studies of synthetic metallohelices, which use hydrogen bonding and
p-stacking interactions predominantly in the formation of secondary structures in
combination with metal-ligand coordination were pioneered in the mid1990s by the
group of A.S. Borovik [19-21]. This group investigated the coordination of metal ions
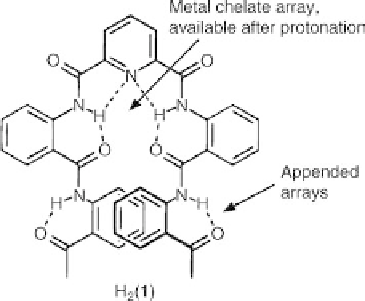
to the multidentate ligand 2,6-bis{[2-({2-acetylphenyl}-carbamoyl)phenyl]carbamoyl}
pyridine, H
2
(
1
) (Figure 11.5). The ligand contains two aryl arrays that are held rigidly
through hydrogen bonds and linked covalently to a pyridyl diamide tridentate chelate.
In the solid state, H
2
(
1
) addopts a helical structure, which is mostly a result of the
hydrogen bonds between the pyridyl nitrogen, the amide protons and the adjacent acyl
oxygens. The ligand was designed such that, upon deprotonation of the pyridyl
amides, a tridentate chelate is formed, enabling the binding of a metal ion via the
pyridine, amides and the acyl oxygens. Due to the weak Lewis base character of these
oxygen donors, it was also anticipated that their interactions with the metal ion would
not depend on the geometric requirements of the ligand but rather on the stereo-
chemical preference of the bonded metal ion. The design of this ligand was therefore
aimed at answering two questions, the first being whether metal coordination could
Figure 11.5 Structure of the multidentate ligand 2,6-bis((2-((2-acetylphenyl)-carbamoyl)
phenyl)carbamoyl)pyridine, H
2
(1). Reprinted with permission from Ref. [20] Copyright 1996
American Chemical Society.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search