Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Fig. 2. Fabrication of bulk PEG-based hydrogels by means of UV-curing.
To ensure a complete reaction of the acrylate end-groups which could otherwise undergo
undesired reactions with the biological system, the curing kinetics of the system were
monitored. It was confirmed that after 10 min more than 90 % of the C-C double bonds of
the acrylate end-groups had been consumed. After 60 min only 2.3 % of unreacted end-
groups were left. Based on these observations it was decided to apply 60 min of UV-
irradiation to the samples in order to achieve virtually complete crosslinking. Bulk PEG-
based substrates were fabricated by casting the prepolymer mixture against a smooth silicon
surface.
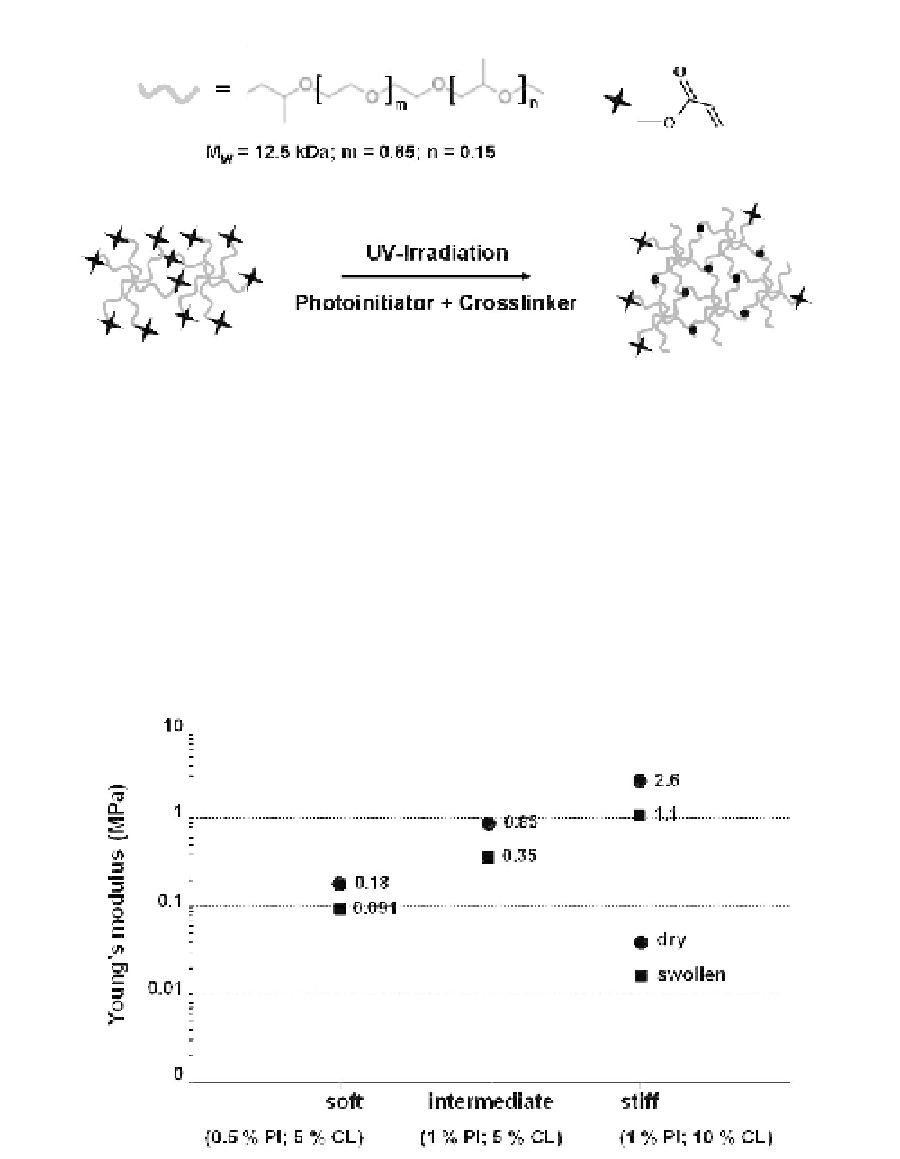
Fig.
3. Young's modulus (MPa) of bulk PEG-based hydrogel samples in dry and swollen
state; gels were fabricated from three precursor mixtures with different percentages (w/v)
of photoinitiator (PI) and crosslinking agent (CL). Reprinted with permission from: Schulte
et al.
Biomacromolecules
,
11,
3375-83. Copyright 2010 American Chemical Society.