Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
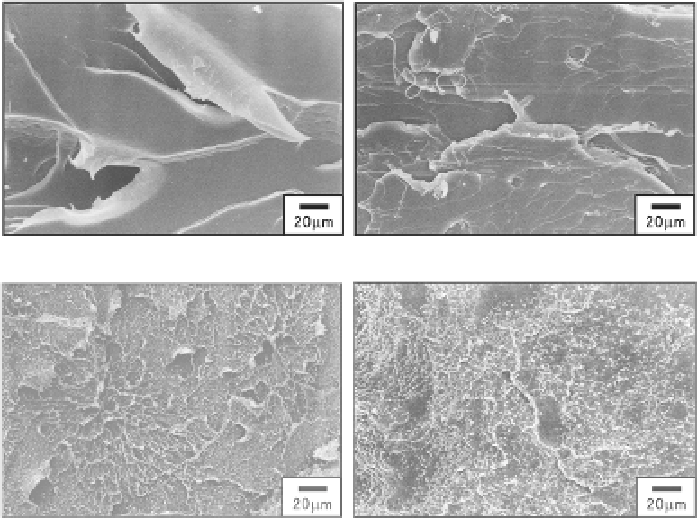
(a)
X
c
=2.7%, static (b)
X
c
=2.7%, impact
(c)
X
c
=55.8%, static (d)
X
c
=55.8%, impact
Fig. 4. FE-SEM micrographs of fracture surfaces.
2.2 Effect of unidirectional drawing process
Drawing process is known to be an effective way to improve the mechanical properties of
thermoplastics, and effects of drawing on tensile and fracture properties of thermoplastics
such as polypropylene (Mohanraj et al., 2003a, 2003b; Uehara et al., 1996), poly(acrylonitrile)
(Sawai et al., 1999; Yamane et al., 1997) and PLA (Todo, 2007) have been studied. PLA is
usually draw-processed when it is used for bone fixation devices, and therefore,
fundamental effect of drawing on its fracture behavior needs to be characterized. As an
example, dependence of draw ratio on the critical
J
-integral at crack initiation,
J
in
, is shown
in Fig.5. In the fracture specimens, the initial notches were introduced in the direction
perpendicular or parallel to the drawing direction. Therefore, the two different types of
specimens are denoted as 'perpendicular' and 'parallel'. For the parallel,
J
in
decreased with
increase of draw ratio, and
J
in
for draw ratio of 2.5 became about one fifth of the original. On
the contrary, for the perpendicular,
J
in
increased as draw ratio increased, and
J
in
for draw
ratio of 2.5 became five times greater than that of the original. Thus, greater energy is
needed for crack propagation in the perpendicular than in the parallel. This is easily
understood by considering the effect of drawing on the micromechanism of fracture. In
draw-processed polymer, molecules are reoriented in the drawing direction. Therefore,
energy dissipation during crack growth by elongation and scission of such oriented
molecules is much greater in the perpendicular direction than in the parallel direction where
such elongation and scission processes obviously decrease.
FE-SEM micrographs of fracture surfaces are shown in Fig. 6. The perpendicular with draw
ratio 2.5 exhibited rougher surface with ductile deformation than the original (without
drawing). It is interesting to note that crevices existed on the fracture surfaces that were
thought to be cracks transversely propagated between the parallel fibrils reoriented in the