Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
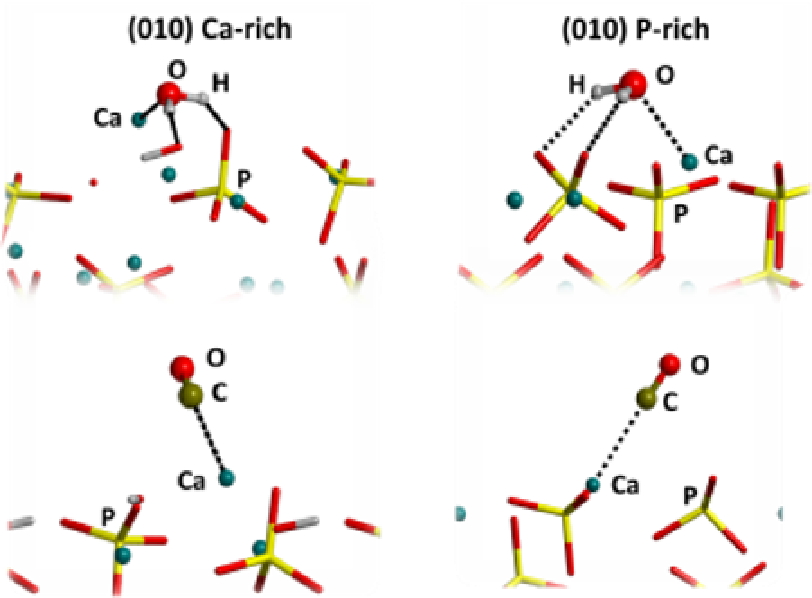
Fig. 4. Best views of the interactions between the most exposed ions of the (010) Ca-rich and
(010) P-rich surfaces and the two probe molecules, water and carbon monoxide. The
interactions with Ca ions and the hydrogen bonds are represented with dotted lines.
The stretching frequency shifts of the CO molecule are 40 cm
-1
for the (010) Ca-rich surface
and 41 cm
-1
for the (010) P-rich surface. These BE and frequency shifts values indicate that
the Ca ion can reasonably be considered as the major cause of the activity of HA towards
polar molecules free from H-bond interactions.
A comparison with the experimental IR spectrum of CO adsorbed on HA reveals two main
components, characterized by an upward shift of the stretching frequency of the adsorbed
molecule of about +27 and +41 cm
-1
, respectively. The highest shift is attributed to a tiny
fraction of the most exposed calcium ions, which are those modeled in our studies, so
proving a good agreement. On the other hand, the majority of calcium sites contribute to the
lowest shift (Bertinetti et al., 2007; Sakhno et al., 2010).
2.1.3 Hydroxyapatite and carbonate ion defects
HA is the main component of the inorganic phase of bones and teeth, but, as many studies
have demonstrated, the mineral present in those tissues is neither crystalline nor without
defects (Fleet & Liu, 2003; Fleet & Liu, 2004; Fleet & Liu, 2007; Rabone & de Leeuw, 2005;
Astala & Stott, 2005; Astala et al., 2006; Rabone & de Leeuw, 2007; de Leeuw et al., 2007 ).
Indeed, it incorporates many other elements, ions or compounds, such as Mg or other
alkaline earth metals instead of Ca, and, above all, the carbonate anion. Many studies, both
theoretical and experimental, have already been conducted on the role of the carbonate ion