Image Processing Reference
In-Depth Information
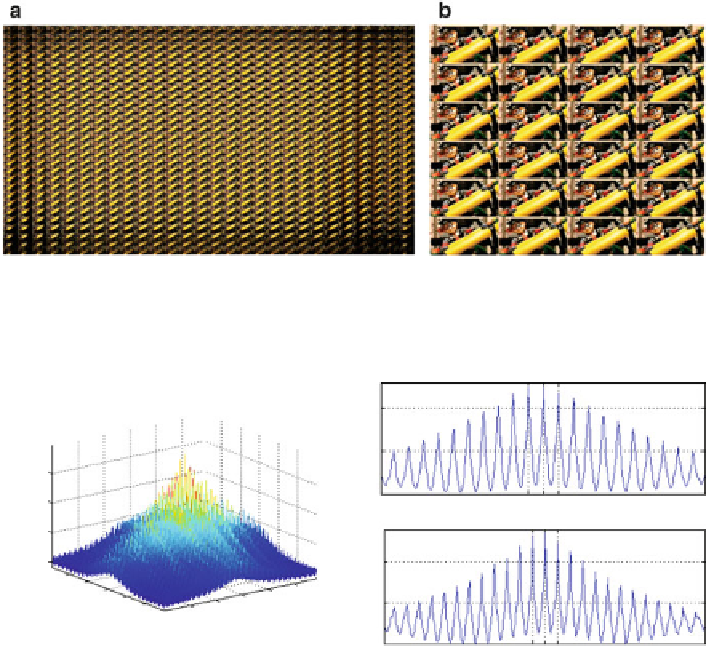
Fig. 5.5 Viewpoint image based representation: (a) VI-based holoscopic image; (b) enlargement
of 272
228 pixels showing each viewpoint image in detail
x 10
4
a
b
1.38
1.32
x 10
4
1.22
1.4
1.12
1.3
-MLAn
MLAn
x
x 10
4
1.2
1.4
1.1
1.32
y
1.22
x
1.12
y
-MLAm
MLAm
Fig. 5.6 Example of spatial correlation in a VI-based holoscopic image: (a) autocorrelation
function; and (b) projection onto x and y axis
be seen in Fig.
5.6
through the autocorrelation function, the pixel correlation in the
VI-based holoscopic image also presents a periodic structure, which is given
approximately by the resolution of each viewpoint
image (represented by
MLA
n
MLA
m
in Fig.
5.6b
).
5.3.3 Ray-Space Image Based Representation
The epipolar-plane technique [
14
] can be used to generate a ray-space image based
representation from the 3D holoscopic image. In this case, a ray-space image can be
formed by stacking together micro-images in the same row/column (in the array of
micro-lenses) and, then, taking a slice from a particular horizontal plane (perpen-
dicular to the micro-lens plane). For example, choosing a row
k
m
in the array of
micro-lenses illustrated in Fig.
5.4a
, and considering that the horizontal plane was