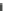Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Fig. 5.19
The volatilization
loss of nitro isobutyl glycerine
trinitrate with time at different
temperature [
5
]
1.0
0.8
80 °C
0.6
0.4
0.2
70
°C
°C
68
0.0
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
14
16
18
20
time(h)
Molecular weight: 286.11
Oxygen balance: 0
Nitrogen content: 19.58 %
Density: 1.6171 g/cm
3
C)
Viscosity: 308.55 centipoises (20
(20
°
°
C)
Freezing point:
C
Refractive index: n
2
d
¼
−
39
°
4896
Formation heat: 702.08 J/g (constant volume) or 200.83 kJ/mol (constant vol-
ume) or 226.35 kJ/mol (constant pressure)
Combustion heat: 2217.52 kJ/mol (constant volume) or 7765.5 J/g (constant
volume)
Vapor pressure and volatility: Less than nitroglycerine. Nitro isobutyl glycerine
trinitrate is little volatile at room temperature without odor. It is slightly volatile at
30
1
:
C with odor of tar and acridity. The volatility is increased at elevated tem-
perature. It is obviously volatile at 50
°
10 mg/
cm/day. The relationship of the volatility of nitro isobutyl glycerine trinitrate and
temperature is shown in Fig.
5.19
and its vapor pressures are listed in Table
5.49
.
The relationship between the surface tension of nitro isobutyl glycerine trinitrate
and temperature is shown in Table
5.50
.
°
C. Its volatility at 25
°
C is 0.127
×
Table 5.49
Vapor pressure of nitro isobutyl glycerine trinitrate [
5
]
Temperature
(
40
50
60
70
80
°
C)
2.74
×
10
−
4
5.00
×
10
−
4
14.8
×
10
−
4
33.6
×
10
−
4
79.3
×
10
−
4
Vapor pres-
sure (mmHg)
Table 5.50
Relationship between the surface tension of nitro isobutyl glycerine trinitrate and
temperature [
5
]
Temperature (
°
C)
20
30
40
50
60