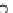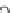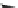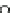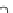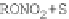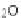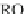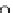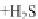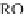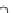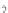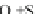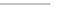Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
HO
!
NO
3
RONO
2
þ
ROH
þ
NO
3
þ
2HS
!
NO
2
þ
HS
2
þ
HO
In the condition of dilute sodium hydroxide solution, the hydrolysis of cellulose
nitrate and primary monohydric alcohol nitrate would be hydrolyzed very slowly.
For example, only 10 % of 0.1 mol butyl nitrate, which was mixed with the solution
of 0.2 mol sodium hydroxide and ethanol (60 %), was hydrolyzed at 27
°
C for 16
days. Even the temperature was elevated to 60
C and the reaction time lasted for
100 h, still only 10 % butyl nitrate was involved in the reaction. However, if sodium
sulfhydrate was added to the reaction system, the butyl nitrate can be completely
hydrolyzed in 4 h.
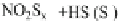
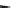
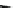
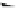
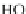
Compared with nitrous acid ions, nitric acid ions can be slowly reduced in
sodium sulfhydrate. The nitrous acid ions are produced from the hydrolysis of
nitrate esters, other than from the reduction of nitric acid ions. Thus, the nitrous acid
ions are formed, most likely, by the breakage of bonds between oxygen and
nitrogen atoms. The effect of sulfhydrate on the hydrolysis of nitrate esters is to
reduce the reactants, as expressed in the following reaction mechanism equations.
°
N bonds would be
broken to form alkoxy and thionitrate ions or polythionitrate ions. The effect of
sul
Because of the activity of sul
ions, and polysul
de ions, O
-
des on the reduction of oxygen atoms should be considered in other same type
reactions. It would form nitrous ions, which cannot be produced from nitrate
reduction.
If hydrazine is involved, nitrate esters act as oxidizers in the explosion reaction.
At high temperature, ethyl nitrate would react with hydrazinobenzene to produce
aminobenzene, ammonium nitrate, and ammonium. If sodium ethoxide is used in
the reaction, even at high temperature, the products would not include nitrous acid
ions, nitrogen, benzene, phenyl azide, azobenzene, nitrobenzene, aminobenzene,
acetic acid, and aldehyde.