Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
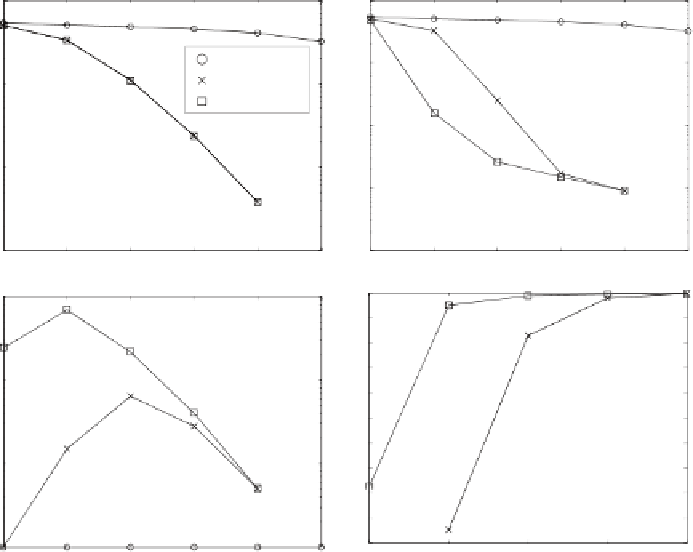
Figure 14.5(a), (b) and (c) respectively shows the total community size
V
X
(
k
)
|}
|
and the number of com-
munities
S
X
(
k
)
for each order
k
for the three core extraction methods.
We can observe that although the statistics of these two networks shown in
Table 14.1 are different, the experimental results of these two networks are quite
similar. Namely, the total sizes of the communities extracted by the
k
-dense
method and the
k
-clique method are the same for each
k
.When4
V
X
(
k
)
|
, the maximum community size max
{|
≤
k
≤
5, the
maximum community size obtained by the
k
-dense method is somewhat larger
than that obtained by the
k
-clique method, while the number of communities
extracted by the
k
-clique method is larger than 100. Finally, the
k
-core method
can extract only one community for each
k
, and the total size of the communities
and the size of the maximum community are larger than a few thousands even
at the maximum order
k
=8.
Figure 14.5(d) shows the normalized entropy
(
X
(
k
)) for each order
k
ob-
tained by the
k
-dense and
k
-clique methods. In this figure, we can observe a
remarkable difference between the two methods when
k
= 4 and the number of
communities obtained by the
k
-clique method is almost one thousand.
E
10
4
10
4
k−core
k−dense
k−clique
k−core
k−dense
k−clique
10
3
(a)
(b)
10
3
10
2
10
2
10
1
10
1
10
0
3
4
5
6
7
8
3
4
5
6
7
8
core order k
core order k
10
3
1
0.9
k−core
k−dense
k−clique
(c)
0.8
0.7
10
2
k−dense
k−clique
0.6
(d)
0.5
0.4
10
1
0.3
0.2
0.1
10
0
0
3
4
5
6
7
3
4
5
6
7
8
core order k
core order k
Fig. 14.5.
Total size of communities (a), size of the maximum community (b), total
number of communities (c), and normalized entropy (d) of the word association network