Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
10
4
10
4
k−core
k−dense
k−clique
k−core
k−dense
k−clique
(a)
(b)
10
3
10
3
10
2
10
2
10
1
10
1
0
5
10
15
20
0
5
10
15
20
core order k
core order k
10
3
1
k−core
k−dense
k−clique
0.9
(c)
0.8
0.7
10
2
0.6
0.5
0.4
10
1
k−core
k−dense
k−clique
0.3
(d)
0.2
0.1
10
0
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
14
0
5
10
15
20
core order k
core order k
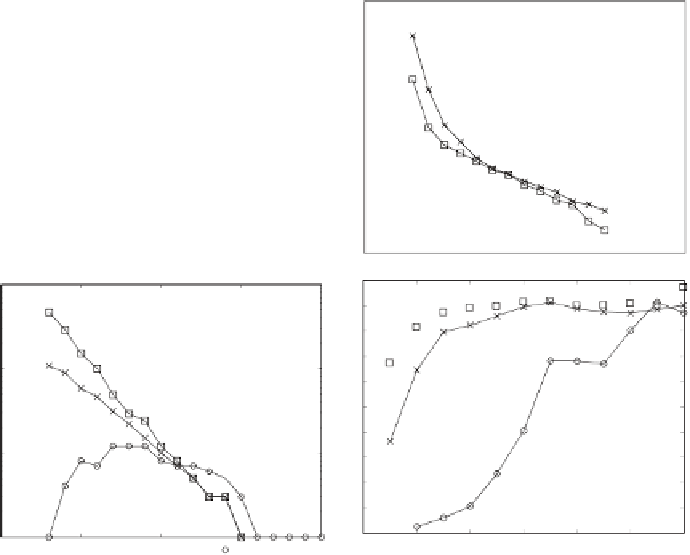
Fig. 14.4.
Total size of communities (a), size of the maximum community (b), total
number of communities (c), and normalized entropy (d) of the blog trackback network
each community is small, which suggests that the
k
-clique method inconveniently
produces a large number of small communities. On the other hand, the number of
communities extracted by the
k
-core method is at most 10, which suggests that it
may be insucient to analyze detailed community structure.
Figure 14.4(d) shows the normalized entropy
(
X
(
k
)) for each order
k
ob-
tained by the
k
-core,
k
-dense and
k
-clique methods respectively. Here only the
results when
k
is in the range of 3
E
14 are displayed because this measure
is valid only when the number of communities is more than one. This figure
indicates that the variance in community sizes is small when extracted by the
k
-
dense method or the
k
-clique method, while the variance is large when extracted
by the
k
-dense method, especially when
k
is small.
≤
k
≤
14.3.3
Evaluation Using the Word Association Network
The
k
-core,
k
-dense and
k
-clique methods are applied to the word association
network labeled
Word
in Table 14.1. The results of the
k
-dense method and the
k
-clique method both show that
k
max
= 7, while the result of the
k
-core method
shows that
k
max
=8.