Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
steady-state condition is, in general, the most critical, at least in terms of amount of
contaminant flux.
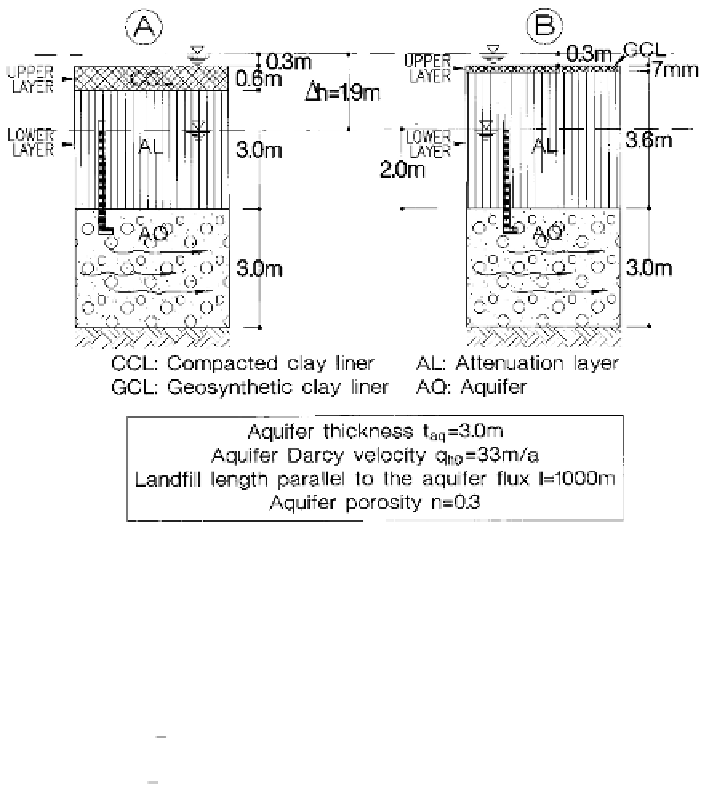
Figure 16.17.
Cross-section of a CCL-based liner and a GCL-based liner
On the basis of the aforementioned assumptions, the current steady-state
contaminant vertical flux,
J
v
, per unit area of the bottom barrier can be represented
by the following equation [MAN 00]:
q
c
⋅
e
−
c
Λ
J
=
q
0
x
[16.2]
v
q
e
−
1
Λ
where:
c
0
: contaminant source concentration (in the leachate);
c
x
: contaminant concentration in the aquifer at a horizontal distance
x
from the
upstream side of the landfill;
q =
Γ∆
h
: Darcy seepage velocity through the barrier; and