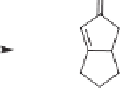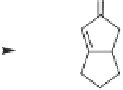Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
OC
CO
CO
Co(CO)
3
Co
(R,R) - 1-2
Toluene, -78 °C
4 A sieves
R
E
R
Z
(CO)
3
Co
(CO)
3
Co
CHO
n
-C
6
H
13
n
-C
6
H
13
OH
13
:R
E
=Me,R
Z
= H (28 % e.e.)
14
:R
E
=H,R
Z
= Me (83 % e.e.)
(88 % e.e. at -90 °C)
12
O
C
6
H
13
(CO)
3
Co
C
6
H
13
SiO
2
,CO
70 °C, 42 h
H
Me
d.r. 23:1
yield 67 %
H
b
(CO)
3
Co
Me
H
a
OH
OH
15
13
(69 % e.e.)
O
C
6
H
13
(CO)
3
Co
C
6
H
13
SiO
2
,CO
65 -70 °C
15 - 20 h
H
Me
H
b
d.r. 11:1
yield 66 %
(CO)
3
Co
H
a
Me
OH
OH
14
(88 % e.e.)
16
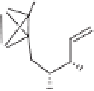
Scheme 4.4
Enantioselective crotylboration of 3-decynal dicobalt hexacarbonyl.
The Pauson-Khand reaction was also successfully applied to the enantioselective
synthesis of (-)-kainic acid and its derivatives, which are known for their anthelmintic
and neuroexcitatory activities. In the first example, Takano
et al.
described a new
enantiospecific route to (-)-kainic acid from (
R
)-4-benzyloxy-l-butyn-3-ol
16
that employs
the intramolecular Pauson-Khand reaction as the key step (Scheme 4.5).
5
Viaafewsteps,
acetylene alcohol
16
was first transformed into corresponding tertiary carbamate
17
in
a 76% overall yield. Subsequent treatment of
17
with dicobalt octacarbonyl furnished
complex
18
in an 82% yield, which was reacted with excess
N
-methylmorpholine
N
-oxide
(NMO) to yield an inseparable mixture of bicyclic enones
18a,b
in a 6:1 diastereomeric
ratio and in an 85% yield. Reduction of the mixture using a complex prepared from lithium
aluminum hydride and copper(I) iodide in THF and HMPA followed by removal of the
THP group in acidic methanol furnished separable adducts
19a
and
19b
. Isomer
19a
was
then used for the enantiospecific synthesis of natural (-)-kainic acid
20.
A similar approach to the enantiospecific synthesis of (-)-kainic acid and its derivatives
was independently developed by Yoo
et al.
The sources of chirality for this method are
optically vinylglycine derivative
21
and L-glutamic acid derivative
27
, respectively.
6
When
enyne
21
was subjected to the Pauson-Khand reaction using dicobalt octacarbonyl followed
by treatment with trimethylamine
N
-oxide or MNO, the reaction proceeded smoothly to
give an inseparable mixture of two diastereoisomers,
22
and
23
, in a 1.7:1 ratio and a 95%
yield. Hydrogenation of the mixture of enones (i.e.,
22
and
23
) resulted in a mixture of ke-
tones
24
and
25
, which were separated using silica gel column chromatography. Treatment
of the major isomer,
24
, using Holton's method regioselectively (97:3 ratio) produced ther-
modynamically more stable enolether
26
, which was used for the enantiospecific synthesis
of (-)-kainic acid (Scheme 4.6).